Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
NH
NH
O
O
N
NH
O
O
NH
NH
N
NH
O
N
NH
O
O
NH
O
N
NH
NH
N
NH
O
O
O
N
NH
O
NH
N
NH
O
N
N
G0
NH
O
G1
G2
G3
Surface
group
Branching
point
Core
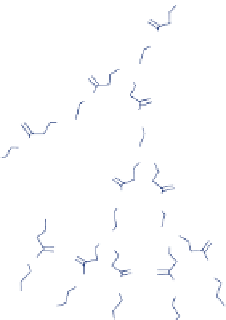
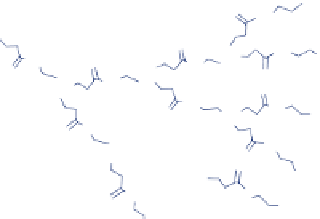
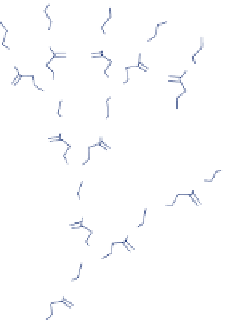
figure 15.7
structure of paMaM dendrimers. (reprinted from ref. [141]. © Wiley.)
on the other hand, covalent conjugation of drugs with dendrimers enables better
control over the drug release, as the labile linkers between drug and dendrimer can
be specifically cleaved under certain tumor microenvironment. This will allow for
reduced systematic toxicity and improved therapeutic efficacy. however, covalent
conjugation involves additional synthetic steps and often requires modification
of drug structure for conjugation reaction. as a result, it has the potential issues of
releasing less active forms of the drug and drug regulations. There has been growing
interest in loading drugs to dendrimers through covalent conjugation due to its
significant advantage of controlled drug release. some examples include MTX-g4
paMaM with an amide linker [147], MTX-g5 polylysine dendrimer with a peptide
linker [148], DoX-paMaM with an acid-labile,
cis
-aconityl linker [149], and pTX-
triazine dendrimer with an ester linker [150].





























































Search WWH ::

Custom Search