Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
(b)
Vimentin
CPMV
HeLa
*
Vimentin
CPMV
nuclei
nuclei
HT-29
Colocalization:
vimentin-CPMV
MDA-
MB-231
Vimentin
CPMV
nuclei
(c)
(d)
CPMV
HT1080 tumor
Merge
(g)
(h)
(e)
(f)
Yo lk sac
Placenta
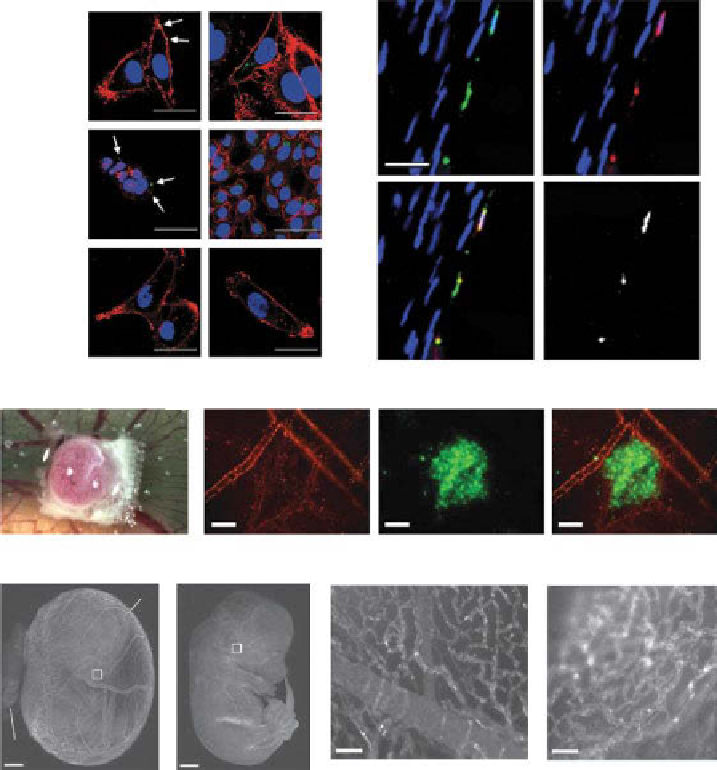
figure 14.3
CpMV has natural affinity for cells through interaction with surface vimen-
tin. (a) Left panel: surface vimentin expression of heLa, hT-29, and MDA-MB-231 cells
(indicated by arrows). Live cell staining was performed using the monoclonal antivimentin
antibody v9. right panel: CpMV-oregon Green 488 (o488) nanoparticles uptake by heLa,
hT-29, and MDA-MB-231 cells. Scale bar is 30 mm. (reproduced with permission from ref.
[54]. © Wiley.). (b) Colocalization of CpMV and surface vimentin on rat aortic endothelium.
Scale bar is 30 mm, and * indicates aorta lumen. (reproduced from ref. [71].) (c) Bright-field
image of hT1080 tumor CAM model after 7 days. Nylon mesh grid is used for angiogenesis
quantification. (d) image of CpMV-A555 lining the vasculature taken right after hT1080 tumor
xenograft was performed (left), GFp-expressing hT1080 tumor (middle), and merged images
(right). Scale bar is 100 µm. (e, f) image of 11.5-day chick embryo injected with CpMV-A555
with yolk sac intact (e) and removed (f). White boxes are of magnified regions shown in (g) and
(h). Scale bar is 1.1 mm. (g, h) Magnified images of yolk sac vasculature and capillaries in the
head region, respectively. Scale bar is 25 µm. (Figure (c-h) were reprinted with permission from
ref. [53]. © Macmillan publishers, Ltd.) (
See insert for color representation of the figure.)
Search WWH ::

Custom Search