Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
have been developed, which do not cause RNAseH activation and confer much greater
stability to the antisense agent (Fig. 13.5). Nucleic acid analogs that have these prop-
erties are 2′-O-alkyl derivatives, thiophosphates, morpholidates (mORF), locked
nucleic acids (LNAs), and PNAs [73-76]. Some of these analogs also show enhanced
B
B
O
O
O
O
N
O
O
P
N
O
P
CH
3
O
CH
3
-
O
Morph
LNA
B
B
O
OR
O
N
O
N
P
O
O
O
H
-
S
PNA
2′-OMe phosphorothioate
NH
2
NH
2
N
O
3′-end
C
O
N
N
N
H
A
N
N
O
G
N
T
N
H
H
N
5′-end
N
N
N
N
H
O
H
H
N
H
H
N
O
N
N
N
N
N
Carboxy
terminus
Amino
terminus
CH
3
O
O
CH
3
N
O
CH
3
Py
Im
Py
β
Polyamides
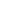
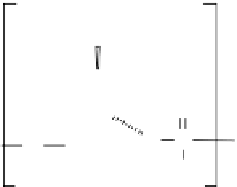
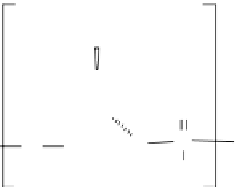
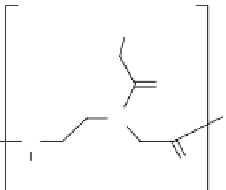
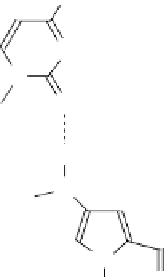
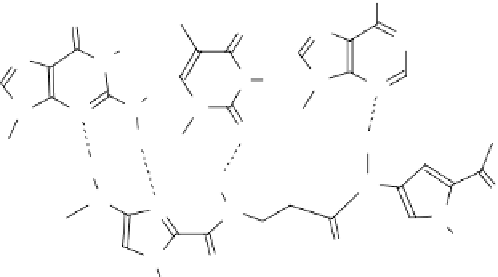
fIgure 13.5
Structure of (a) degradation-resistant antisense nucleic acid analogs and (b)
the antigene polyamides that recognize a double-stranded DNA sequence through hydrogen
bonding interactions in the minor groove.
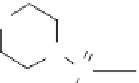









Search WWH ::

Custom Search