Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
(b)
(c)
Gas bubbles
escaping
diving bell
Mouse
Prism
Nd. YAG
laser
Tunable
dye-laser
Mirror
Laser
z
Ground glass
x
Trigger
Stop motor
y
Membrane
Water
PC
Concave lens
Ground glass
Membrane
Water
tank
Gas
proportioner
meter
O
2
+ N
2
+ CO
2
Oscilloscope
Fiber bundle
Breathing mask
Transducer
Animal
holder
Pre stressed
berglass rods
Black tape
cer array
Oxygen tube
Amplier
Probe
PA
image
(d)
(e)
Hemi
spherical
US array
US
image
US
system
DAQ
US probe
Scanning
stage
Hand held
PA/US probe
Fiber bundles
Dye laser
Nd: YAG laser
Laser
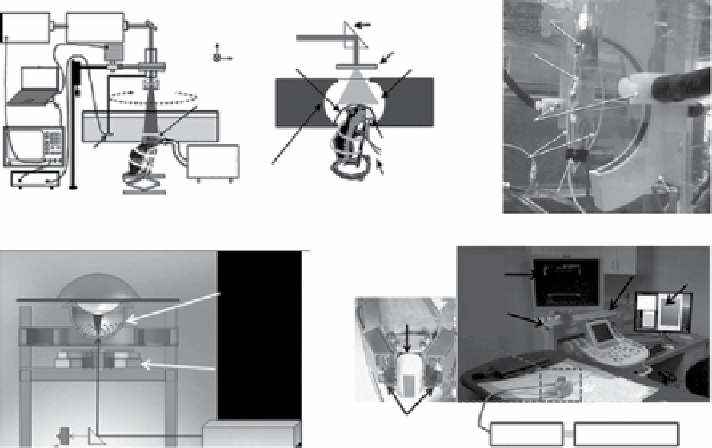
figure 10.2
Various types of PACT systems implemented by (a) a single-element ultra-
sound transducer with 360° full circular mechanical scanning (reprinted with permission from
ref. [69]. © SPIE, (b) a full-ring ultrasound array (reprinted with permission from ref. [70]. ©
SPIE, (c) an arc-shaped ultrasound array (reprinted with permission from ref. [71]. © SPIE
(reprinted with permission from ref. [72]. © optical Society of America, (d) a hemisphere
ultrasound array, and (e) a handheld probe modified from a clinical ultrasound array system.
(reprinted with permission from ref. [40]. © The American Association of Physicists Medicine.)
was greatly improved to a frame rate of 0.9 Hz (Fig. 10.2b) [70, 73]. Using this
system, functional brain [70] and whole-body imaging [74] of small animals have
been successfully performed. As another example, an arc array (64 elements and a
central frequency of 5 MHz) was implemented to provide whole-body imaging of
rodents (Fig. 10.2c) [71]. The acquisition time of one three-dimensional (3d) image
was 8 min. To further enhance clinical translation, clinically friendly PACT systems
have been recently developed such as tomographic PA breast scanners and linear-
array-based PA probes. Figure 10.2d shows the schematic of a tomographic PA and
US breast scanner consisting of 128 US elements with a center frequency of 5 MHz
[72]. This system can be potentially used to screen early stage of breast cancer
patients and map breast angiography. In addition, a handheld PA and US probe
(Fig. 10.2e), modified from a clinical US system (Philips iU22), is currently used in
phase I clinical studies to monitor early response of chemotherapy and identify
sentinel lymph nodes in breast cancer patients [40, 41]. The second type, PAM,
uses a single-element focused US transducer to directly collect one-dimensional
(1d) depth-sensitive images (referred to as A-lines) and 2d/3d images with
mechanical or optical raster scanning [50, 61, 62, 75]. Hardware-based acoustic or
optical focusing provides the transverse resolution, whereas the acoustic bandwidth
Search WWH ::

Custom Search