Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
The degree of labeling could be determined either from material balance during the
synthesis or directly from the optical spectra of the nanoparticles [50, 51]. Quenching
of the fluorophore on the nanoparticles is universal and has been described in a great
number of publications [52-54]. Such quenching is a result of the aforementioned
H-type aggregation [55] as well as other effects [56] and decreases the quantum yield
to virtually zero. This leads to a very low brightness of the imaging nanoparticles.
6.7.2.1 Molar Absorptivity of Nanoparticles
Molar absorptivity of organic fluo-
rophores is generally determined from linear standard absorption plots using the
Beer-lambert law. for nanoparticles with several attached fluorophores (fluores-
cently labeled polymers, dendrimers, dye-loaded liposomes, and nanocapsules), the
absorption properties are nonlinear, and the spectra differ for each individual fluoro-
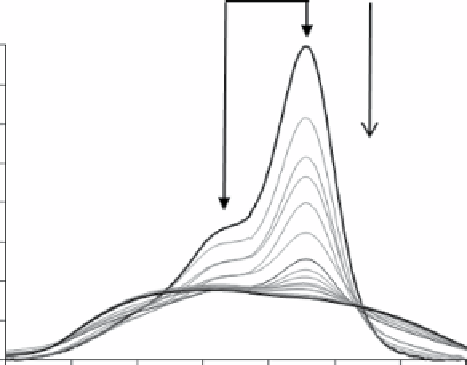
phore type. This is especially apparent in NIR cyanine dyes that tend to form
H-aggregates (H for hypsochromic shift), which have distorted (broadened)
absorption spectra [55] (an example is shown in fig. 6.21). Such spectral behavior is
similar to the known self-assembly of dyes in aqueous solutions where at high con-
centrations the individual monomers are aligned parallel to each other in a face-to-face
arrangement [57, 58]. Due to the similarity between nanoparticles and concentrated
solutions, unknown molar absorptivity of optical nanoparticles can be deduced from
a set of concentration-dependent molar absorptivity spectra. This can be done by
matching the shape of the nanoparticle spectrum to the spectrum of a sample with a
known concentration. alternatively, a ratio of the H-band intensity to the intensity of
the absorption maximum can be used.
Ratio
Increased
conc.
160,000
140,000
120,000
100,000
80,000
60,000
40,000
20,000
0
550
600
650
700
750
800
850
900
Wavelength (nm)
figure 6.21
Molar absorptivities of a NIR dye in water with increasing concentration of
the dye from 0.1 to 20 μM concentration.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search