Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
(b)
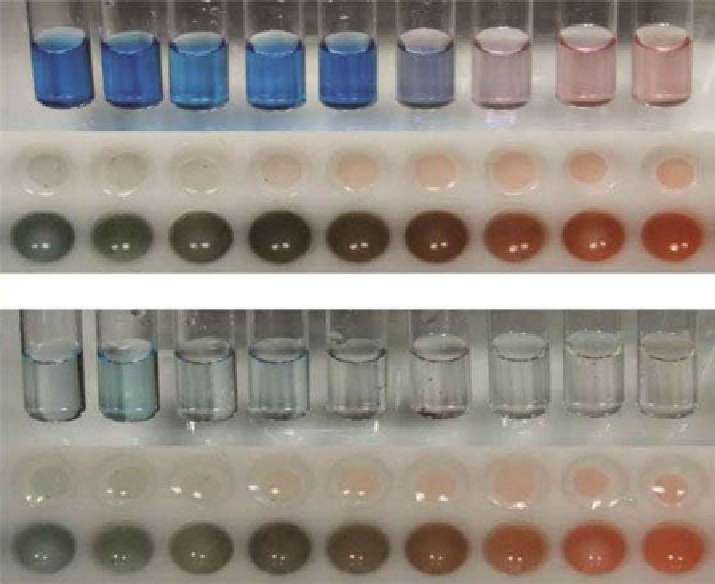
Figure 4.12
Photostability of Nile Blue (NB) A free and when encapsulated in porous
NCs in buffers solutions with pH values ranging between pH 2.5 and 12.5. (a) Photos of
freshly prepared solutions, microplate wells filled with PVA-based hydrogel specimens in
which the NB A-loaded NCs are dispensed, and microplate wells filled with buffer solutions
of different pH values in which the NB A-loaded NCs are dispensed. (b) Photographs of the
same solutions and wells after 2 weeks of storage under regular laboratory conditions. The pH
in the test tubes and wells labeled 1 through 9 was set to pH 2.5, 3.5, 5.5, 6.5, 9.5, 10.0, 10.5,
11.5, and 12.5 using citrate- (1, 2), mES-(2-(
N
-morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid) (3, 4), borate-
(5, 6, 7), and phosphate-based (8, 9) buffers, respectively. (Adapted with permission from Ref.
[65]. © American Chemical Society.)
2.5
3.5
4.5
5.5
6.5
7.5
8.5
9.5
11.5
12.5
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0.0
A
(a)
(b)
C
B
(c)
A
BC
600 650 700
400 450 500 550
Wavelength (nm)
2.5
3.5
4.5
5.5
6.5
7.5
8.5
9.5
11.5
12.5
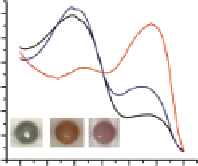
Figure 4.13
Aqueous suspensions and uV-Vis spectra (at pH 7.5) of NCs containing NB
with β-CD sulfonate (a) NB and (b) NB with tetraphenyl borate (c) at different pH. (Adapted
with permission from Ref. [65]. © American Chemical Society.)


Search WWH ::

Custom Search