Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
short
long
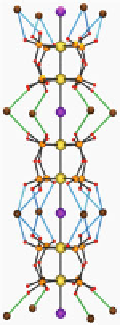
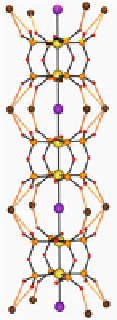
Fig. 10.5 Chain structure of K
2
(NC
3
N)[Pt
2
(pop)
4
I]
4H
2
O(
left
) and K
2
(NC
5
N)[Pt
2
(pop)
4
I]
4H
2
O
(
right
) with the representation of colored K-O(pop) coordination bonds
The twisting of pop ligands induces two different coordination features between
two [Pt
2
(pop)
4
] units and A
+
, that is, monodentate and bidentate coordination to A
+
,
as shown in Fig.
10.5
.
d
(Pt-I-Pt) is different between each coordination feature. On
the other hand, K
2
(NC
5
N)[Pt
2
(pop)
4
I]
4H
2
O, which is in CDW state, has equal
coordination features (two monodentate and two bidentate coordination to A
+
)
between two [Pt
2
(pop)
4
] units (Fig.
10.5
), resulting in the unique
d
(Pt-I-Pt).
Consequently, the different coordination bonds induced by the twisting of pop
ligands are the origin of the ACP-like distortion.
10.2.4 Electronic Structure of ACP + CDW State
The optical conductivity spectra were measured to reveal the detailed electronic
structure of MMX chains with binary countercations [
31
]. Photon energy of the
peaks in the spectra are summarized in Table
10.3
.
Optical conductivity spectra of all measured MMX chains with binary
countercations consisted of the strong lowest charge transfer (CT) band around
1 eV (indicated by boldface) and weak bands around 2.2 eV, 3.2 eV, and 3.9 eV. It
has been known that the photon energy of CT (
E
CT
) increases with an increase of
Pt-I-Pt distance (
d
(Pt-I-Pt)) in CDW and CP states of pop-type MMX chains, and
that the dependency of
E
CT
on
d
(Pt-I-Pt) in CDW state is larger than that in CP
state because the inter-dimer CT in CDW state is more sensitive to
d
(Pt-I-Pt) than
is the intra-dimer CT in CP state [
51
]. This dependence of
E
CT
on
d
(Pt-I-Pt) was
applied to the phase diagram of CDW and CP states. Figure
10.6
shows the phase
diagram of already-known MMX chains together with the plots of complexes
in Table
10.3
. It should be noted that
the average value of two kinds of




Search WWH ::

Custom Search