Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
ready_in
read
R
Q
valid_out
S
write
valid_in
ready_out
data_ou
t
1
DQ
data_in
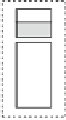
Fig. 2.8
The pipelined EB that offers full throughput of data transfer and introduces direct
combinational paths between ready_in and ready_out backward notification signals
read
ready_in
R
Q
valid_out
S
write
valid_in
ready_out
data_out
1
data_in
DQ
Fig. 2.9
The bypass EB that offers full throughput of data transfer and introduces direct
combinational paths between data_in (valid_in) and data_out (valid_out) forward signals
valid data, assuming that an enqueue is performed in the same cycle (dequeue on
empty if enqueue). In order for the incoming data to be available to the output of
the BEB on the same cycle, a data bypass path is required as shown in Fig.
2.9
.The
bypass condition is only met when the EB is empty. In the case of the BEB, the
priority of the R-S state flip flop is given to Reset.
Both buffers solve the low bandwidth problem of the HBEB and can propagate
data forward at full throughput. However, certain handshake signals propagate via





















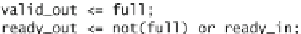












































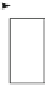












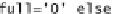








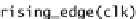


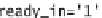



































Search WWH ::

Custom Search