Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
update[2]
update[1]
update[0]
credit
counters
a
ready[0]
ready[1]
ready[2]
ready
valid
data
sender
receiver
b
credit
counters
update
ready
valid
data
sender
receiver
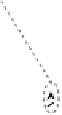
Fig. 6.3
The abstract flow control model enhanced for supporting virtual channels. One free slot
(or credit) counter is added per VC that can be placed either at the receiver or at the sender. Multiple
ready signals can be asserted per cycle showing which VCs is ready to accept new flits. In the
simplest case only one VC will leave the receiver and update the status of the corresponding VC
buffer
the id of the VC that returns a new credit; the encoding minimizes the flow control
wires to 1
C
log
2
V in each direction. This is possible since at most one VC will send
valid data to the receiver and the receiver will drain at most one flit for its buffers
thus updating the status of only one credit counter. Thus, in each direction a single
valid/update bit is used and a VCid that encodes the index of the selected VC in
log
2
V bits; the VCids arriving at the receiver via the valid signals and at the sender
via the update signals should be first decoded before being used in either side of
the link. The complete list of wires used in a physical channel that accommodates
V VCs is shown in Fig.
6.4
, including also the appropriate packet framing signals
isHead and isTail that are used to describe the id of the flit that is currently on
the link.
The basic property of VC-based flow control is the interleaving of flits of
different packets. In each cycle, a flit from a different VC can be selected and appear
on the link after having consumed its corresponding credit. The flit once it arrives
at the receiver is placed at the appropriate VC buffer indexed by the VC ID of the
forward valid signals. Since the buffering resources of each VC at the receiver's side
are completely separated, interleaving the flits of different packets does not create
any problems, assuming that the VC-based flow control mechanism does not involve












































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search