Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
Reading
Manchester
Birmingham
Aldershot
Crawley
Leeds
Cambridge
Bristol
Nottingham
Liverpool
Milton Keynes
High Wycombe
Newcastle
Oxford
Luton
Blackpool
Warrington
Telford
Bournemouth
Sheffield
Brighton
Sunderland
Basingstoke
Derby
Southampton
Southend
Wigan
Coventry
Northampton
Ipswich
Peterborough
York
Warwick
Bath
Birkenhead
Darlington
Stoke
Hull
Leicester
Norwich
Swindon
Blackburn
Exeter
Middlesbrough
Halifax
Plymouth
Bedford
Mansfield
Chesterfield
Lincoln
Hartlepool
Torbay
Portsmouth
-2,000
0
2,000
4,000
6,000
8,000
10,000
12,000
14,000
16,000
18,000
Numerical change in ICT employees
Note:
Dei nition of computer and related ICT services - 1992 SIC category 72.
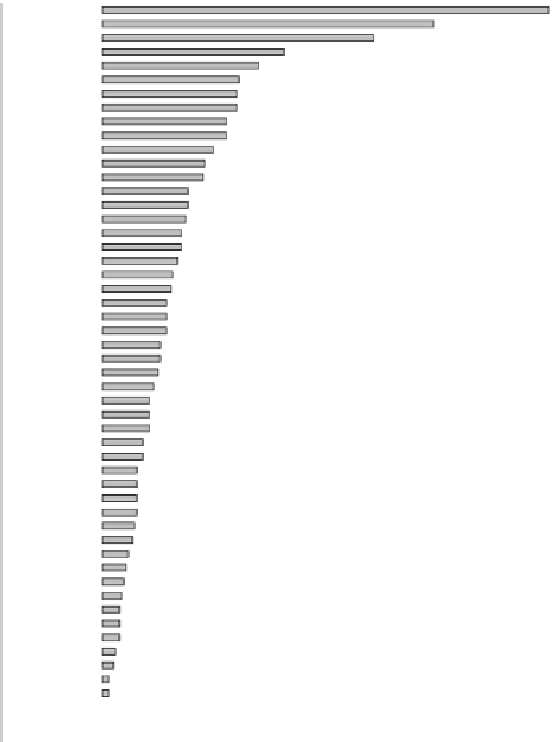
Figure 23
.
2
Absolute change in ICT employees 1991-2002 (excluding London)
In England, information systems and the kinds of service sector whose main functions
are the enabling and exchange of information have developed and evolved at dif erent
rates in dif erent locations. Recent research (Simmie et al., 2006), commissioned by the
Oi ce of the Deputy Prime Minister (ODPM), has examined the factors underlying the
competitiveness of the economies of the 56 largest cities in England with populations
exceeding 125,000. The locations and extent of the 'travel to work areas' (TTWAs) of
these cities are shown in Appendix 1.
As part of this analysis the rates of change in employment in the ICT sector were
examined. Figure 23.2 shows the absolute changes in ICT employment (SIC 72) between
1991 and 2002. The i gure excludes London where the growth was 90,806 as compared