Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
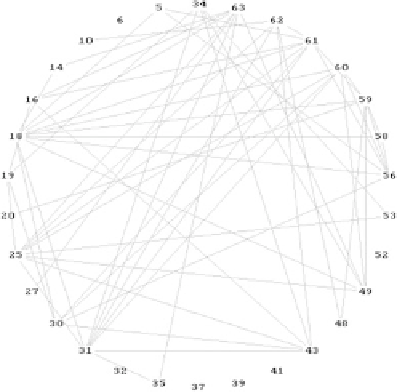
Figure 13
.
4
Knowledge sharing in Cortina
In a similar way:
n
n
(
(
CT
ji
*
WC
i
)
CT
ji
*
WC
i
)
CR
j
5
a
0
i
i
51
1
CR
j
network
size
CR
j
= competence-based reputation of node '
j
' (where 0 <
RR
j
< 1)
CT
ji
= ef ective competence-based trust relation of node '
j
' with node '
i
' (1 = activated;
0 = not activated)
WC
i
= node's weight in terms of competence-based trust centrality (where 0 <
WC
i
<
1)
network
size
The dataset was processed in two ways: i rst, three separate statistical analyses, one for
each local network - Bormio, Cortina d'Ampezzo and Pila - were worked out; second,
the entire dataset - as an aggregate of all data - was processed. Table 13.2 shows the
statistical results of correlation analysis between relational reputation and centrality of a
single actor inside the network.
5
The relational density value can be presented only in the
case of the three ef ective networks, while it is a meaningless indicator for the analysis of
the entire dataset.
These i ndings seem to coni rm the following hypothesis:
(Hp1)
There is a positive correlation between the degree of relational reputation and
degree of centrality of a single actor inside the network
.
The correlation between relational reputation and centrality for the entire dataset is
quite signii cant (0.4116) and its control test coni rms this result (
p
- value <0.0001).
6
It
means that network-specii c resources inl uence i rm variety in terms of social dynam-
ics. Figure 13.5 shows the QQ plot related to this result and highlights a positive trend
especially in the central part of the graph.