Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
highly depleted in volatile and moderately volatile litho-
phile elements. Whole-rock oxygen isotopic compositions
of CH chondrites are similar to CR chondrites, suggesting
they may have formed from a common oxygen reservoir,
and nitrogen isotopic compositions show remarkable
positive anomalies in N, with δ
15
N up to ~800 ‰ [
Krot
et al.
, 2002;
Weisberg et al
., 1989].
The CB (Bencubbin-like) metal-rich chondrites (Plates 21
to 23) also have characteristics that are sharply different
from other chondrites [
Weisberg et al
., 2001]. The Antarctic
CB chondrites have given us the opportunity to establish
and study this group and its intergroup variations. The
characteristics of CB chondrites include (1) high metal
abundances (60-80 vol.% metal); (2) most chondrules have
cryptocrystalline or barred textures; (3) moderately volatile
lithophile elements are highly depleted; and (4) nitrogen is
enriched in the heavy isotope. Additionally, most CB chon-
drites contain areas of impact-produced melt between the
silicate and metal consisting of silicate glass with tiny
(<1 µm) immiscible blebs of FeNi metal or vice versa.
Termed spontaneous fusion texture by
Newsom and Drake
(1979) and interpreted to be melted chondrite matrix by
Meibom et al
. (2005), these regions attest to the major role
that impact played in the history of the CB parent asteroid.
Similarities in mineral composition, as well as oxygen and
nitrogen isotopic compositions of the CB to CR and CH
chondrites, are consistent with derivation of these chon-
drite groups from a common nebular reservoir, hence their
grouping in the CR clan [
Weisberg et al.
, 1989, 2001;
Weisberg and Prinz
, 1999;
Krot et al
., 2002]. A close rela-
tionship between CB and CH is strongly supported by the
Ischeyevo chondrite, which appears to be a mixture of CH
and CB lithologies [
Krot et al
., 2006;
Ivanova et al
., 2009].
The CB chondrites have been divided into two subgroups,
CB
a
and CB
b
, based on their petrologic characteristics
[
Weisberg et al
., 2001]. The CB
a
chondrites contain ~60 vol%
metal, chondrules are centimeter-size, FeNi metal ranges
from 5 % to 8 % Ni, and bulk δ
15
N values are up to ~1000‰,
whereas the CB
b
contain >70 vol % metal, their chondrules
are millimeter-size, their FeNi metal contains 4 to 15 % Ni,
and δ
15
N compositions are ~200 ‰. See
Weisberg et al.
[2001] for detailed description and discussion of the CB
chondrite subgroups. The Antarctic meteorite collection
has provided samples of both CB
a
(MIL 05082) and CB
b
(QUE 94411) chondrites (Figure 4.3a; Plates 21 and 22) and
thus has helped define the CB group and establish its
subgroups.
The origin and relationship of CH and CB chondrites
to other chondrites is an open issue. Their chondrules and
other components have been interpreted to form in the
early solar nebula [e.g.,
Newsom and Drake
, 1979;
Weisberg
et al.
, 1989;
Weisberg et al
., 2001;
Meibom et al
., 1999;
Krot et al.
, 2002;
Campbell et al
., 2001] or as products of
late-stage planetesimal collisions in the early solar system
(a)
QUE 94627, 3
100
μ
m
(b)
QUE 94411
Ni Ka X-ray
Zoned
Silicate
Zoned
metal
Troilite
Zoned
Silicate
Zoned
Silicate
500
μ
m
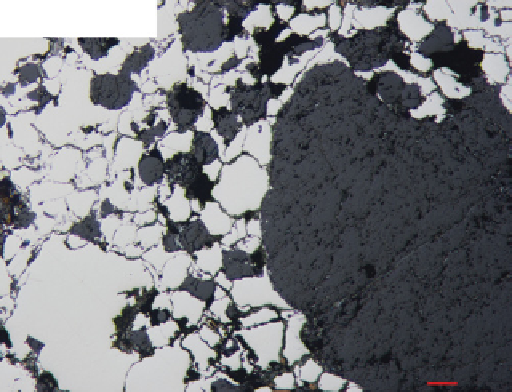
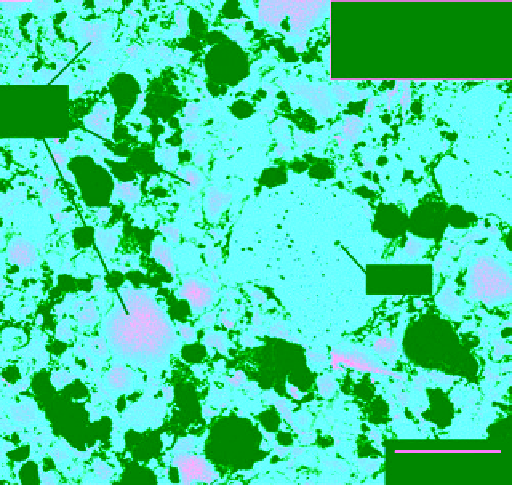
Figure 4.3.
(a) A reflected light photomicrograph of QUE
94627,3 (paired with QUE 94411), a CB
b
chondrite. The section
shows a large cryptocrystalline chondrule (dark gray), smaller
chondrules (<100 µm in size), and abundant FeNi metal (white).
(b) A Ni Kα x-ray image of QUE 94411 showing composition-
ally zoned metal grains (bright) that decrease in Ni content
(brightness) toward the grain edges. Silicates appear black.
Source:
Weisberg et al.
[2001].
[e.g.,
Wasson and Kallemeyn
, 1990;
Campbell et al
., 2002;
Amelin and Krot
, 2005;
Krot et al
., 2005]. The later hypo-
thesis stresses the importance of collision in the early solar
system and the possibility of such collisions as a mecha-
nism for chondrule formation. Continued discoveries of
new metal-rich chondrites for detailed study could help
resolve the issue of their origin.