Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
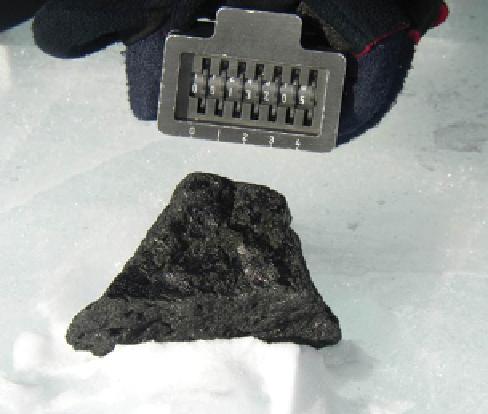
Nakhlite
715.2 g
Found December 15, 2003
10.0 × 6.0 × 5.5 cm
Weathering = B
Nakhlites are clinopyroxene-rich cumulate rocks thought to be from Mars,
based on the composition of trapped noble gases, their young ages (1.3 ga),
and their o isotopic composition. The eight different nakhlites recognized
in our collections are apparently from one magmatic body that shows
textural variation from deeper cumulate-rich to shallower mesostasis-rich
lithologies. Studies of nakhlites have provided constraints on the differen-
tiation history of Mars, the high oxidation state of the mantle, surficial
volatiles such as S, C, and Cl, and organic geochemistry.
50
μ
m
Cl
K
Ti
Aug
Glass
Amph + Smect
Aug
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
10
Fe
8
6
4
2
0
A20 40
Distance (
μ
m)
60
B
Plate 74
MiNERALogy
SigNiFiCANCE
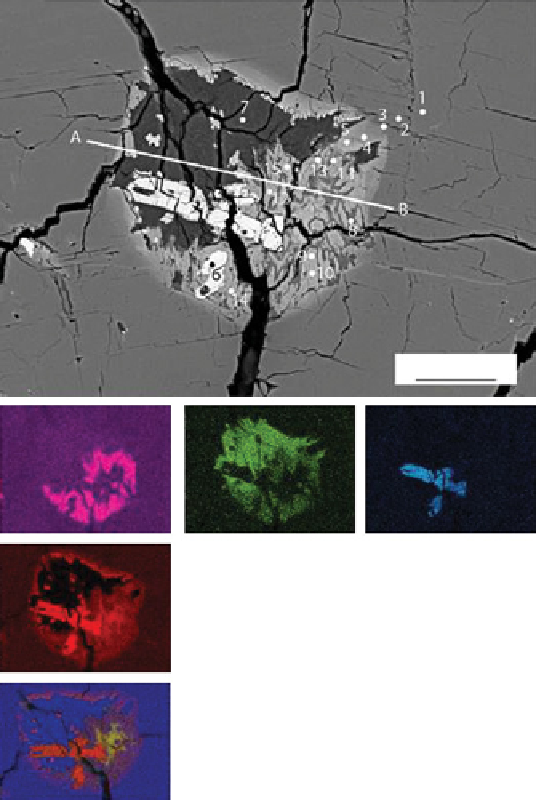
MiL03346 is composed of ~80% clinopyroxene, ~1%
olivine, and ~20% vitrophyric intercumulus material
(skeletal Fe-Ti oxide, fayalite, and sulfide), which suggests
rapid cooling in a shallow intrusion or a lava flow. olivines
contain trapped melt inclusions (top right, [801]).
MiL 03346 crystallized 1.3 ga ago, from a shallow
oxidized magma that may have had a deeper origin. The
textures and chemical compositions suggest it cooled
quickly in a thin flow or dike. After emplacement, it was
shocked only mildly based on its density and magnetism.
Weathering at the surface of Mars produced Cl-amphibole
(bottom right, [801]), jarosite, and other oxidized min-
erals. The pyroxenes have been used to better understand
remote sensing at the surface of Mars.
References [782-803]