Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
Lunar basaltic regolith breccia
30.7, 53.0 g
Found December 20, 1987 and
December 14, 1996
3.7 × 2.5 × 2.0; 4.5 × 3.5 × 1.5 cm
Weathering = A
Although lunar geology is dominated by two end members (mare basalt
and anorthositic crust), there are polymict breccias that represent more
complex rock units and provide information about lunar geologic
processes that cannot be discovered in
Apollo
/
Luna
collections. Polymict
lunar breccias are more rare and provide information about diversity of
materials in Moon rocks.
Breccia
4
Bulk
3
40
Basalt
2
Highlands meteorites
FAN suite
Mg-suite
Mare basalt meteorites
A-12 low-Ti mare basalts
A-15 low-Ti mare basalts
EET 96008
EET 87521
35
1
30
EET 96008
0
25
Highland
rocks
400
20
300
15
Mare
basalts
10
200
5
100
0
0
2000
4000
6000
0
Cr (ppm)
0.0
0.2
0.4 0.6
Cumulative
39
Ar fraction
0.8
1. 0
Plate 65
MiNERALogy
SigNiFiCANCE
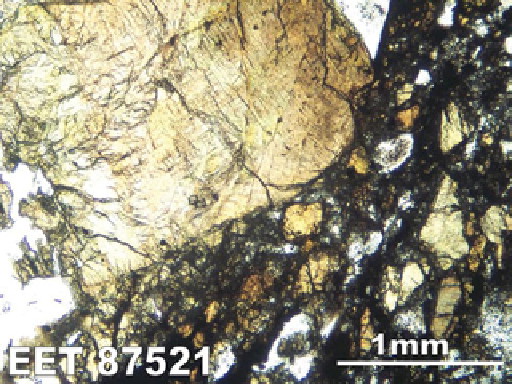
EET 87521 is a polymict regolith breccia that contains
clasts of low Ti mare basalt, high Ti mare basalt, granu-
litic breccia, cumulate breccia, impact melt, anorthosite
(An
90-92
), norite, and troctolite. it also contains many soil
components (regolith breccia and agglutinate) and mineral
and glass fragments.
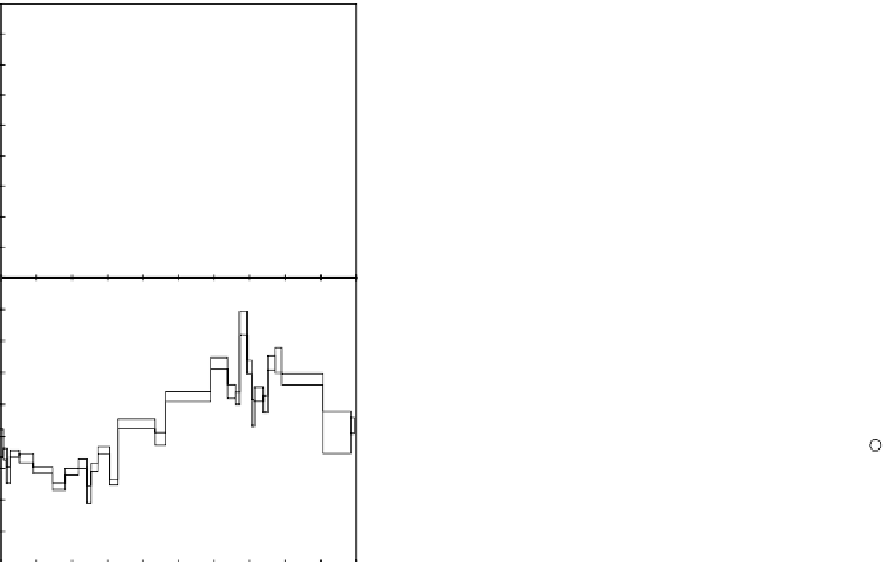
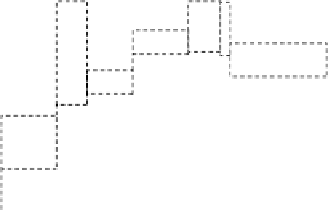
The basaltic clasts found in EET 87521 and 96008 exhibit
young ages that overlap with those of
Apollo
basalts (left,
[494]). However, the overall composition of the breccia
falls intermediate between the basalt and feldspathic
(anorthositic) end members of the lunar geology (right,
[490]), illustrating the diversity of materials and thus the rich
geologic information present in mingled lunar breccias.
References [490-499]