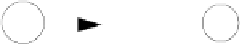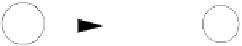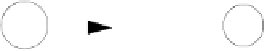Java Reference
In-Depth Information
R
R | S
S
Original Transitions
Combined Transition
(a) The T1 Transformation
X Y
X
Y
X
Y
s
r
u
s
r
u
Original Transitions
Bypass Transition Added
(b) The T2 Transformation
*
X Z Y
X
Y
Y
X
s
u
r
s
r
u
Z
Z
Original Transitions
Bypass Transition Added
(c) The T3 Transformation
Figure 3.30: The
T
1,
T
2, and
T
3 transformations.
requirements, then we can easily transform it by adding a new start state and a
new accepting state linked to the original automaton with
λ
transitions. This is
illustrated in Figure 3.29 using the FA we created with M
in
Section 3.8.2. We define three simple transformations,
T
1,
T
2, and
T
3, that will
allow us to progressively simplify FAs. The first, illustrated in Figure 3.30(a),
notes that if there are two di
ake
D
eterministic
erent transitions between the same pair of states,
with one transition labeled
R
and the other labeled
S
, then we can replace the
two transitions with a new transition labeled
R
|
S
.
T
1 simply reflects that we
can choose to use either the first transition
or
the second.
Transformation
T
2, illustrated in Figure 3.30(b) allows us to
bypass
a state.
That is, if state
s
has a transition to state
r
labeled
X
and state
r
has a transition
to state
u
labeled
Y
, then we can go directly from state
s
ff
to state
u
with a
transition labeled
XY
.
Transformation
T
3, illustrated in Figure 3.30(c), is similar to transformation