Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
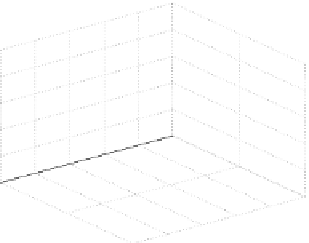
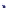
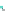
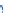
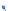
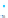
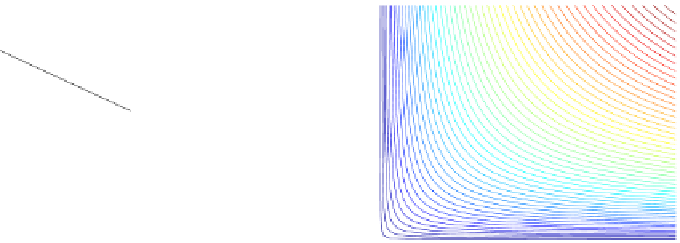
Fig. 14.1
Clayton copula (
14.6
)in
d
=
2for
ϑ
=
0
.
5(
top
)and
ϑ
=
1
.
5(
bottom
)
(iii) Clayton Lévy copulas
2
2
−
d
d
u
i
|
−
ϑ
−
1
ϑ
η
1
,
F(u
1
,...,u
d
)
=
1
|
}
−
(
1
−
η)
1
{
u
1
···
u
d
≥
0
{
u
1
···
u
d
≤
0
}
i
=
(14.6)
where
ϑ>
0 and
η
∈[
0
,
1
]
.For
η
=
1 and
ϑ
→
0,
F
converges to the indepen-
dence Lévy copula, for
η
to the complete dependence Lévy
copula. In Fig.
14.1
, the Clayton copula in
d
=
1 and
ϑ
→∞
=
2for
ϑ
=
0
.
5
,
1
.
5 and
η
=
1is
plotted. We include the upper bound min
{|
u
1
|
,
|
u
2
|}
and additionally give the
corresponding contour plot.
An important class of Lévy copulas are the so-called 1-homogeneous copulas.
Definition 14.2.10
A Lévy copula is called 1-homogeneous if for any
r>
0the
following holds:
F(ru
1
,...,ru
d
)
=
rF(u
1
,...,u
d
),
for all
(u
1
,...,u
d
)
∈ R
d
.























































































































































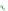







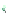














































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































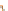























































































































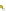



























































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































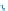






















































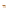










































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































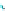


















































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































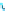
















































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































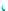

























































































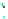






















































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search