Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
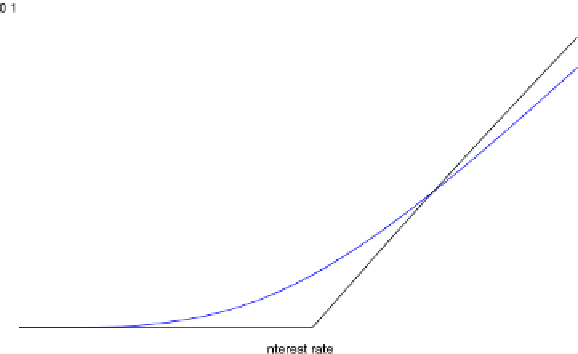
Fig. 7.2
Swaption price in the CIR model
Example 7.2.3
Consider the CIR model with parameters
α
=
0
.
05,
β
=
0
.
2,
σ
=
0
.
3,
K
=
0
.
05 and tenor structure
T
1
=
0
.
25,
T
2
=
0
.
5,
T
3
=
0
.
75,
T
4
=
1,
T
5
=
1
.
5,
...
,
T
10
=
4.TheswaptionpriceisshowninFig.
7.2
.
Remark 7.2.4
A widely used extension of the models described above is the con-
sideration of a deterministic shift function, i.e. instead of considering the solution
r
t
of (
7.1
), the short rate model
r
t
+
ϕ
t
is considered. This extension can be fitted
to any observed term structure. The pricing of derivatives in the extended model is
analogous to the described method applying a change of variable.
7.3 Further Reading
For an introduction to interest rate models, we refer to Brigo and Mercurio [29]. Li-
bor market models in the Lévy setting were considered by Eberlein and Özkan [60].
For theoretical results, we refer to Keller-Ressel et al. [101]. The equations arising
in this context can be solved as described in Chap. 10. Recently, forward rate mod-
els have received significant attention, we refer to Carmona and Tehranchi [31] and
Hepperger [78] for details. Keller-Ressel and Steiner [102] consider attainable yield
curve shapes in an affine setting.


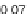


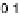


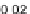
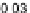







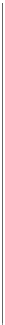
































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search