Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
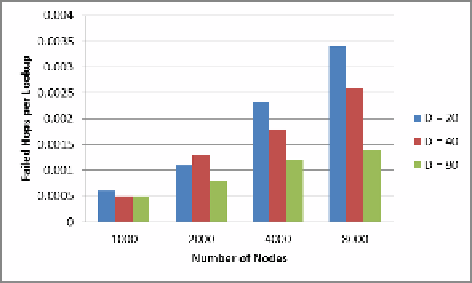
Fig. 7.
Failed rates per lookup varying nodes' number and domains' number
As well as average routing hops, failed lookup rate increased along with the system
size, this is also because more nodes leaving and joining brings about more time delay
to keep routing tables up to date, inaccurate routing tables increase the failed proba-
bility of failure. On the other hand, small domains number also results in a high failed
rate, this is due to few domains generates a big domain size, Comb runs a one-hop
protocol within the domain, failed rate increased along with the domain size because
of the time delay for routing tables up to date as mentioned before. Therefore, tra-
deoffs should be made between average routing hops and failed lookup rate on the
selection of domains number, generally, the optimal number for minimum traffic we
calculated in section 4 is a good choice. Figure 6 and Figure 7 demonstrate that Comb
has an excellent performance in routing efficiency.
6
Conclusions
This paper presents Comb, a two-hop DHT lookup algorithm for P2P overlay and
evaluates Comb by analysis and experiments. Comb algorithm aims at the features of
the distributed communication system: real-time response and geographic partition,
constructs the whole overlay a two-layered architecture. Nodes in Comb system main-
tain two routing tables: local table and global table, messages are routed intra-domain
and inter-domains.
Compared with other DHT lookup algorithms, the main contributions of Comb are:
a non-hierarchical two-layer DHT architecture that avoids unbalanced workload and
bottlenecks; a two-hop routing mechanism that routes most lookups in no more than
two hops to satisfy the real-time response requirement; a domain-partition mechanism
that adapts the geographic distribution pattern of distributed communication system;
an improved message dissemination mechanism--binary-multicast tree that balances
the workload in disseminating of each node and an abstract model for network traffic
calculation.