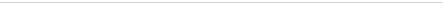Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
3500
NEPSO
RTAA
M CTTA A
3000
2500
2000
1500
1000
500
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
Number of Alliances
Fig. 4.
The life cycle of different numbers of coalitions
5
Conclusion
For certain characteristics of wireless sensor networks, based on dynamic coalition
mechanism, this paper propose a task dynamic allocation algorithm using game
theory. The proposed algorithm designs a strategy to solve the Nash equilibrium with
PSO algorithm. Simulation results show that the adaptive algorithm constructed in
this paper is effective. It can obtain a satisfactory solution in a short time and ensure
the execution time while effectively extend the lifetime of network. Further research
work will focus on the fault-tolerant mechanism, namely, building a tasks adaptive
allocation algorithm with fault-tolerant mechanism in WSN.
Acknowledgements.
This work was supported in part by the National Natural
Science Foundation of China under Grant No.61103175 and No. 61103194, the Key
Project of Chinese Ministry of Education under Grant No.212086, the Technology
Innovation Platform Project of Fujian Province under Grant No.2009J1007, the Key
Project Development Foundation of Education Committee of Fujian province under
Grand No. JA11011, and the Fujian Province High School Science Fund for
Distinguished Young Scholars under Grand No.JA12016.
References
1.
Akyildiz, I.F., Su, W., Sankarasubramaniam, Y., et al.: Wireless sensor networks: a sur-
vey. Computer Networks 38, 393-422 (2002)
2.
Yu, Y., Viktor, K.P.: Energy-balanced task allocation for collaborative processing in wire-
less sensor networks. Mobile Networks and Applications 10(12), 115-131 (2005)