Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
3.4 LabelCast Processing
The Labelcast rules of five tuples include the restriction field of resources, which
indicates the resources that network applications could use. Each LabelCast node
allocates computing resource, storage and network bandwidth to network appli-
cations based on the LabelCast rules issued by LabelCast controller, which real-
ize the resources sharing between network experiments. LabelCast nodes adopt
eXtensible Linux Container to manage resources and allocate computing time,
storage size and network bandwidth to the container based on the restriction
field of rules, which provides the dedicated resources for network applications.
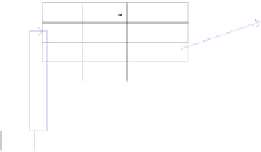
Fig. 3.
Processing Model of Labelcast
The network application registers the network protocol of packets to the La-
belcast controller firstly, and the Labelcast controller allocates the subspace of
the label space to the application, as illustrated in Fig.3. When packets arrived
at the Labelcast node, the Label table are lookup against the label in Labelcast
options of packets. The first packet of flows with default label could be sent to
the Labelcast controller due to unmatching against the Label table. The Label-
cast controller dispatched the packet to the network application, which register
the network protocol type. The network application allocates the label from the
subspace and assigns the label to the flow, and make the process policy for the
flow. Based on the label and the policy the Labelcast controller generates rules
and configure the Label table and Cast table, and then notify the rules to the
upstream and downstream nodes. At the same time, the Labelcast controller
notify the label to the source node of the flow. After the configuration, the host
send the following packets of the flow with the label, which are marked by the