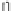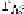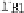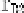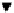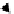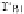Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 2.
An example of Dom-C in multi-domain systems
Fig. 3.
An example of Mig-C in multi-domain systems
SoD-C is one of the most frequently occurred conflict type in VRBAC as well
as in other RBAC models. It occurs when one's access has been permitted and
denied to a resource simultaneously. This contradiction would lead to unautho-
rized access and malfunction of cross-domain interoperation. This conflict can
be denoted as
SOD
−
C
,weget
SOD
−
C
=
{
(
r
1
,r
2
)
|∃
u
∃
res
(
u
∈
Users
∧
res
∈
Resources
∧
u
∈
assign
(
r
1
)
∧
u
∈
assign
(
r
2
))
∧
diff
(
policy
(
r
1
,res
)
.action
,
policy
(
r
2
,res
)
.action
))
,where
assign
means all users assigned with the role.
In Fig. 4, we provide an example of an interoperation generated by merging
the access control policies of different domains. From the inheritance hierar-
chy semantics we can see that
r
A
1
indirectly inherits
r
B
1
by role mappings of
r
A1
ₒ
}
r
A3
and r
A3
ₒ
r
B1
, at the same time
r
A
1
also inherits
r
B
2
via role
mappings of r
A1
ₒ
r
B
2
. However, in Domain B, the
assignments of
r
B
1
and
r
B
2
for virtual machine
v
B
1
are opposite from each other,
like one permitted and another denied. This would lead to uncertain policy en-
forcement in
r
A
1
and could even cause far more serious danger like unauthorized
accesses.
r
A4
,r
A4
ₒ
r
A5
and r
A5
ₒ
4.2 Conflict Checking Approach
At the conflict checking phase, We choose OWL-DL, a type of ontology language
to describe our model and conflicts, then use Description Logic (DL), one of the
most promising reasoning technique to reason them. The knowledge base of
DL contains two parts: TBox and ABox. TBox specifies the field terminology
knowledge, while ABox offers the assertions about instances of TBox. We'd like