Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
2.4 Optimization Models of MIMC
Besides the above heuristic design, there are also theoretical analysis and op-
timization models of using multi-interface multi-channel (MIMC) architecture
[3,7,21]. These models usually require the topology and tra
c to keep steady
for the algorithms to converge. This makes them only fit for mesh network with
static topology and known trac pattern. And they will have diculty in highly
dynamic scenarios, such as in VANETs.
In mobile scenarios, channel assignment is usually solved using heuristics (such
as [9,23]). Our work is also a heuristic design. But we first find the connectivity
invariant condition. The consequent channel usage based multichannel design
is simplified and more ecient. The detail analysis and design are given in the
following two sections.
3 Connectivity Invariant Condition
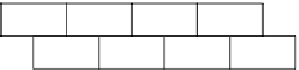
In our previous work, we have designed a connectivity invariant multichannel
assignment method based on road map topology (MIMC-Road)[24]. In MIMC-
Road, the road is divided into multiple channel segments in a staggered pattern
(as shown in fig 2). This staggered pattern can guarantee that any two vehicles
within the communication range will sit in one of the common channel segments.
Thus the network connectivity with the multichannel configuration is identical to
the single channel network. The vehicles select their active channels according to
the position information, and switch the channels when they move to the other
channel segments. But this method has the following shortcomings. First, the
channel assignment is static according to the position. When the density is high
and several vehicles are in the same channel segment, they cannot adapt to the
different channels. Second, for those idle vehicles that are not communicating,
they also need to switch the channels when they move across the channel segment
boundaries. Furthermore, all the interfaces shall have the similar communication
ranges to make the multichannel segment division easy and effective.
Communication
Range
Chanel Sequence
for Interface 0
CH 0
CH 1
CH 2
CH 0
...
Chanel Sequence
for Interface 1
CH 2
CH 0
CH 1
CH 2
...
CH 2
CH 0
CH 1 CH 0
Road
Fig. 2.
A MIMC-Road example of 3 channels and 2 interfaces of each node