Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 1.
(
Continued
)
Port_ID
(physical/virtual)
is_ virtual
(first column)
Node_ID, Port_MAC, is_active, is_edge_port,
VLAN_ID, throughput
Node_capbility
protocol_name, version, port
Reachability
IP_prefixes, length
Node_table_ID
(Flow entity)
Columns names are the same as the fields defined in the flowtable in
OpenFlow specification
Link_Utilities
Link_ID, Link utilities
Flow_path
(Node_ID_src_
Node_ID_dst)
Port_ID (in), Node_ID_src, Port_ID (out),
Node Series with ingress and egress ports,
Port_ID (in), Node_ID_dst, Port_ID (out)
The edge in the table above refers whether this entity is the edge of a domain. Each
domain uses the edge information to construct a global network view. The node, link,
and port can be a physical entity or a virtual entity.
•
Network View Learning.
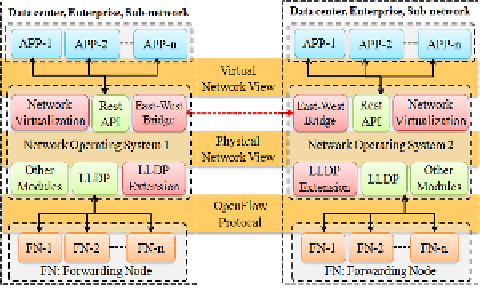
The basic information such as node, node_capbility, port, and link information usual-
ly can be learned by the LLDP (Link Layer Discovery Protocol). To learn more net-
work view information such as OpenFlow version and number of the FlowTables on
each node, link utilities, and flow entries, we extended the NOS by adding a network
view driver module named LLDP extension shown in Figure 2. All the network view
information is provided to network applications by Rest API. We can enable EW-
bridge in all kinds of NOSes by adding the three modules in the red color shown in
Figure 2. Network virtualization and east-west bridge module will be showed later.
Fig. 2.
Enable EWBridge in all kinds of NOSes by adding three modules (Network Virtualiz-
tion, East-West Bridge, and LLDP Extension)