Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
properties. Therefore, many efforts have been done for improving their properties by
blending some filler [7].
Among the natural biopolymers, polysaccharides seem to be the most promising
materials in various biomedical fi elds. These biopolymers have various resource in-
cluding animal origin, plant origin, algal origin, and microbial origin. Among various
polysaccharides, CS is the most usual due to its chemical structure [8].
Chitosan
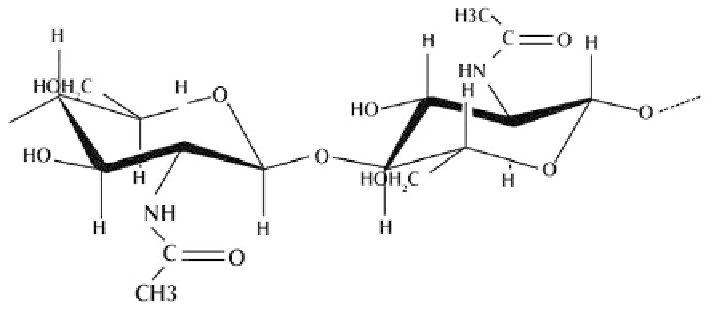
Chitin (Fig. 7.1) is the second most abundant natural polymer in the world and extracted
from various plant and animals [9]. However, derivations of chitin have been noticed
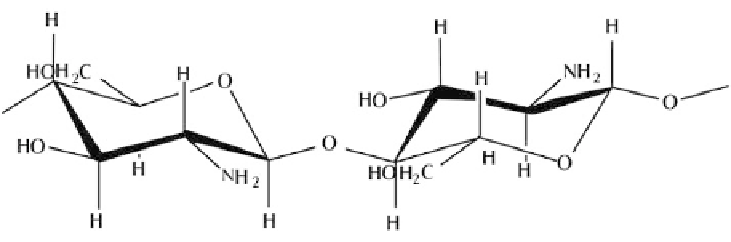
due to insolubility of chitin in aqueous media. CS (Fig. 7.2) is deacetylated derivation
of chitin with the form of free amine. Unlike chitin, CS is soluble in diluted acids and
organic acids. Polysaccharides are containing 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-β-D-glucose and
2-amino-2-deoxy-β-D-glucose. Deacetylation of chitin converts acetamide groups to
amino groups [10]. Degree of deacetylation (DD) is one of the important effective pa-
rameters in CS properties and has been defined as “the mole fraction of deacetylated
units in the polymer chain” [11].
Figure 7.1.
Structure of chitin.
Figure 7.2.
Structure of chitosan.
















Search WWH ::

Custom Search