Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
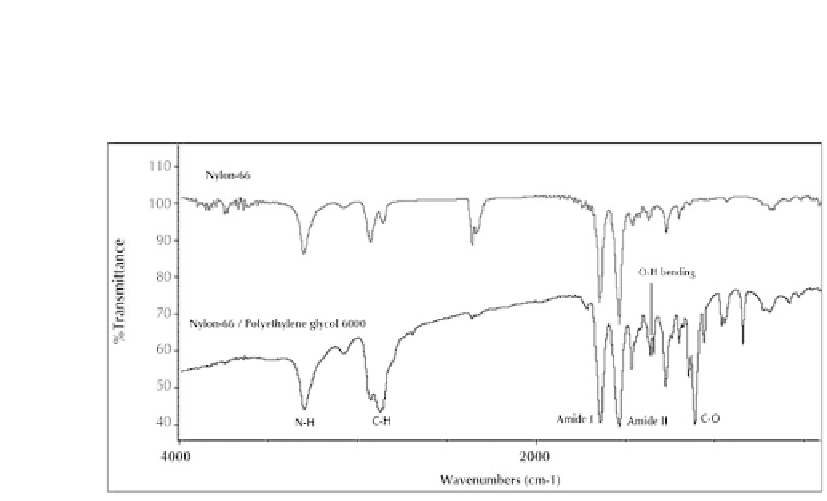
to C-O-C stretching. These two last peaks indicate the existence of PEG between the
polymer chains of nylon 6,6 and prove that the composite sample in fact is a PCM/
polymer nanofibrous structure.
Figure 6.4.
FTIR spectra of Nylon 6,6 and Nylon 6,6/PEG nanofibers.
Thermal Properties of Electrospun Nanofibers
In order to analyze the thermal properties of nylon 6,6/PEG nanofiber, pure nylon 6,6
nanofiber mat, and nylon 6,6/PEG nanofiber mats at the blend ratio of 100/50 and
100/130 were chosen. Their DSC thermograms are shown in Fig. 6.5. It is clear that
the pure nylon 6,6 nanofiber mat has no phase change peak, no heat capacity, and
therefore no ability to heat storage. However, nylon 6,6/PEG samples have melting
and crystallization peak. Phase change points and latent heat of phase changes are
shown in Table 6.2. It is clear that increasing PEG content in the blend nanofibers has
a little effect on the phase change temperatures, but strongly affects the latent heat of
phase changes. Figure 6.6 summarizes the theoretical and the experimental values of
the latent heat for the blend nanofibers. From the theoretical point of view, the en-
thalpy values of nylon 6,6/PEG composite nanofibers calculated by multiplying the
latent heats of pure PEG and its mass percentage in the composite structure. Figure 6.6
shows that all the experimental values were lower than their corresponding theoreti-
cal values. It can be explained by retardation of crystallization process of PEG in the
composite structure during electrospinning; because firstly, the cooling of nanofiber
and evaporating of solvent during the moving of jet through the air gap did not let the
molecular chains of PEG to form a fine crystalline structure in the nanofiber due to
being taken place in a little fraction of a second; and secondly, the hydrogen bonding
between the hydroxyl group of PEG and carbonyl group of nylon 6,6 also hindered
the crystallization process. So, it is concluded that the crystalline areas of PEG in the
composite nanofibrous structure are very tiny and encircled by hydrogen bondings.
These led to lower crystalline areas of PEG and higher deviation of enthalpies from
theoretical values. It is worthy to state that the diluents effect of nylon 6,6 in the com-
posite structure also affects the variation of enthalpy values.















Search WWH ::

Custom Search