Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
1.2 Type of Ion Channels
Ion channels, along with transporter proteins, display a huge diversity in terms of
their structure and topology. Busch W. and co-workers were therefore able to
establish the transporter classification system in 2002 to easily summarize structural
information for researchers [
12
].
Ion channels can be classified by the nature of their gating mechanism, for
instance, the voltage-gated ion channels, ligand-gated ion channels, and other
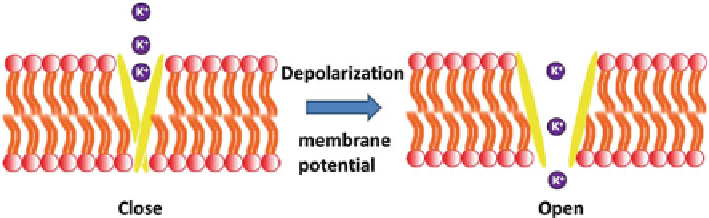
gating ion channels. Voltage-gated ion channels are activated in response to
depolarization of membrane potential [
13
]. When conformational change to the
open state occurs, ions become permeable [
14
]. In the resting or closed channel
state, repolarization of the membrane potential leads to reduced microscopic
currents [
15
].
Voltage-gated ion channels show selectivity toward ions; Na
+
,K
+
, and Ca
2+
channels (Figs.
1
and
2
). Positively charged residues located on transmembrane
segment S4 act as the voltage sensor leading to the alteration of gate currents and
conformational change [
16
]. Ligand-gated ion channels mostly exist in pentamer.
Several types of ligand-gated ion channels are found, however, the evolutionary
tree of 106 sequences of ligand-gated ion channels had been generated by Ortells O.
M. and co-workers in 1995 [
17
]. Ligand-gated ion channels are activated by
Fig. 1 An illustration of the voltage-gated potassium channel in closed and opened state
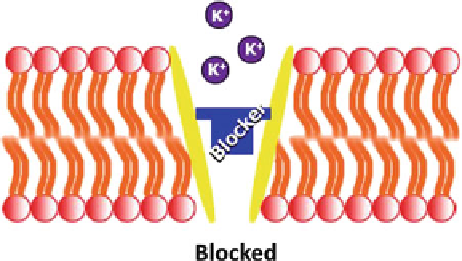
Fig. 2 An illustration of the voltage-gated potassium channel blocker such as R(+)-bupivacaine