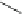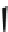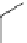Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
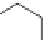
The most potent compounds are present in the scaffold D group (D1 and D2),
shown in Fig.
3
. The contribution of the electronic environment of the descriptor
S_sssN in these two compounds has similar chemical features, as reflected in its
R- and X- substitutions. The presence of this descriptor is very important for the
potent activity of these compounds, which was further confirmed by the positive
slope in QSAR model [
71
]. Further, the functional groups attached at the R region
in compounds D1 and D2 have aromatic features, and do not completely follow the
nature of the chemical environment of the Atype_N_68 descriptor. In other words,
compound D1 has aliphatic amine groups, which are secondary in nature and do not
strictly follow the Al
3
N manner. In support of this observation, this descriptor also
showed a negative slope in QSAR model [
71
].
The scaffold D group also has the least potent compound D3 shown in Fig.
3
with an IC
50
value of 13
M, which is 1,000-fold less potent than compound D1.
The presence of an Atype_N_68 descriptor type chemical feature might be the key
point determining the low activity of compound D3. In compound D3, the R-Me
group substitution is strictly in accordance with the chemical nature of the
Atype_N_68 descriptor. This compound also has two other substitutions with
the same chemical features in the X-region, favoring lower activity [
71
,
82
].
We also analyzed the contribution of different descriptor values in QSAR model
for S_sssN and Atype_N_68 descriptors, w.r.t the most potent compounds D1 and D2
as well as that of the least potent compound D3. These values were usedmainly for the
development of QSARmodel and are very significant in distinguishing between potent
and less potent NCC blockers. The details of these analyses are reported earlier [
71
].
2D-QSAR modeling can help in determining which parts of a compound can be
modified to increase affinity and efficacy, providing valuable guidance in the drug
m
O
O
H
N
H
N
N
N
N
H
N
O
O
BnO
OBn
D1
(0.04 µM)
D2
(0.09 µM)
O
H
N
N
N
O
N
BnO
D3
(13.0 µM)
Fig. 3 Chemical structure of the two most potent N-type Ca
2+
channel blockers D1 and D2, and
least potent blocker D3 (From [82]. With permission from Elsevier)