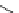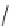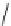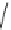Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 14 KYS05090
O
NH
N
N
N
N
Lee et al. [
105
] performed 3D QSAR studies on a set of 42 3,4-dihydroqui-
nazolines using a comparative molecular field similarity indices analyses
(CoMSIA) method, to find out the pharmacophore elements for T-type calcium
channel blocking activity. The derived 3D QSAR model provided good predictivity
for the training set (
q
2
0.642,
r
2
0.874) and the test set (
r
2
pred
¼
¼
¼
0.884) and
can be used for the design of new chemical entities with high T-type calcium
channel blocking activity.
A set of 24 isoxazolyl compounds potent T-type calcium channel blockers
served to establish Comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA) and compara-
tive molecular similarity indices analysis (CoMSIA) [
106
]. CoMFA and CoMSIA
contour maps were used to analyze the structural features of the ligands accounting
for the activity in terms of positively contributing physicochemical properties:
steric, electrostatic, hydrophobic, and hydrogen bonding fields. All CoMFA and
CoMSIA models gave cross-validated
r
2
(
q
2
) value of more than 0.5 and conven-
tional
r
2
value of more than 0.85.
As a result, the efforts for the discovery of new T-type calcium channel blockers
have been intensified [
105
-
108
].
2.2.4 Differences Among Calcium Ion Channel Blockers Side Effects
Calcium ion channel blockers differ in their duration of action, the process by which
they are eliminated from the body and most importantly, in their ability to affect
heart rate and contraction. Some of them e.g.,
amlodipine
, have very little effect on
heart rate and contraction so they are safer to use in individuals who have heart
failure or bradycardia.
Verapami
l and
diltiazem
have the greatest effects on the
heart and reduce the strength and rate of contraction.
2.2.5 Side Effects
Many unwanted effects are related to the vasodilatory effects of Ca
2
þ
channel
blockers, such as flushing, headache, dizziness, and hypotension. DHPs frequently
cause edema and ankle swelling upon chronic use. Worsening of angina has also
been observed with dihydropyridines. This is most likely due to their pronounced