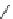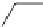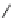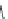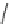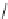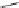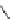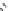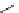Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
OCH
3
OCH
3
OCH
3
OCH
3
N
N
N
N
H
3
CO
H
3
CO
H
3
CO
H
3
CO
OCH
3
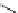
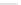
Verapamil
Gallopamil
Fig. 11 Structures of verapamil and gallopamil
OCH
3
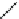
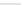
Fig. 12 Diltiazem and
analogs
5
6
R
1
R
2
S
S
R
4
O
H
O
8
N
3
9
N
2
O
1
R
3
Diltiazem
Analogs
N
Benzothiazepines
Benzothiazepines in terms of selectivity for vascular calcium ion channels consist
an intermediate class between phenylalkylamines and dihydropyridines. Since
they have both cardiac depressant and vasodilator activities, they are able to reduce
arterial pressure without producing the same degree of reflex cardiac stimulation
caused by dihydropyridines.
Diltiazem (cardizem) and clentiazem are the main representatives of this class of
calcium ion channel blockers (Fig.
12
).
Diltiazem, a 1,5-benzothiazepine, has affinity for the
L
-type calcium channels
like the other calcium ion channel blockers, but it is less potent on the peripheral
smooth muscle than on myocardial tissue. This weak selectivity produces negative
chronotropic and inotropic effects that reduce the myocardial oxygen demand [
89
].
Negative inotropic potency of 60 benzothiazepine-like calcium entry blockers,
Diltiazem analogs, was successfully modeled using Bayesian regularized genetic
neural networks (BRGNNs) and 2D autocorrelation vectors. The analysis of the
network inputs pointed out to the electronegativity and polarizability 2D topologi-
cal distributions at substructural fragments of sizes 3 and 4 as the most relevant
features governing the nonlinear modeling of the negative inotropic potency.