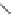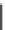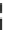Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
NO
2
NO
2
R
1
= Me, Et
n = 2-7
R
1
OOC
COOR
1
COO(CH
2
)n
OOC
N
H
N
H
Me
Me
Me
Me
Fig. 10 Bis-1,4-dihydropyridines
Their biological results were used in quantitative structure-activity relationship
studies utilizing multiple linear regression analysis. For this purpose, a wide range
of descriptors were used such as quantum chemical, topological, functional, elec-
tronic, and constitutional. A total of 120 descriptors were calculated for each
molecule. Most of these compounds were less active compared with nifedipine.
Increase in steric hindrance resulted decrease in activity. The quantitative
structure-activity relationship study indicated that the activity was related to the
electrostatic and topological parameters and the distance between two C-5 esteric
groups of 1, 4-dihydropyridine rings.
Partial least squares [
76
], principal component analysis [
77
] and the gene
expression programming were employed [
78
], using theoretically derived
descriptors for different DHPs analogs. In addition, the quantum chemical QSAR
study indicated the importance of electronic features of the dihydropyridine
derivatives for receptor binding [
79
].
Yao et al. [
80
] used the least squares support vector machine (LSSVM)
algorithm to develop quantitative and classification models for a series of 1,
4-dihydropyridine calcium channel antagonists [
81
], as a potential screening mech-
anism. Each compound was represented by calculated structural descriptors that
encode constitutional, topological, geometrical, electrostatic, quantum-chemical
features. The heuristic method was then used to search the descriptor space and
select the descriptors responsible for activity. Quantitative modeling resulted in a
nonlinear, seven-descriptor model based on LSSVM with mean-square errors
0.2593, a predicted correlation coefficient 0.8696, and a cross-validated correlation
coefficient 0.8167. In the linear model, there were two topological descriptors, one
geometric descriptor, three quantum chemical descriptors and one electrostatic
descriptor.
Compared with classical QSAR investigations, 3D QSAR approaches yield
better results. A 3D QSAR study (comparative molecular field analysis and com-
parative molecular similarity studies) of 4-phenyl-substituted dihydropyridines
indicated unfavorable steric interactions for bulky moieties in the
para-
position
of the phenyl ring and that bulky substituents are favorable in
ortho
- and
meta
-
positions. The best combination is obtained when the bulky substituents at
ortho
-
or
meta-
positions produce negatively charged electrostatic potential. From these
studies was indicated that repulsive electronic interaction with binding-site residue