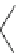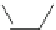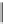Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 2 Fragments related
to strong hERG inhibition
N
N
N
O
N
N
N
N
N
Pattern 1
Pattern 2
the descriptors selected for the threshold at 1
m
M are specific cases of the
descriptors selected for the threshold at 40
M. The fragments ACH
2
AACH
2
A
and ACH
2
AAACH
2
A are related to the global descriptor SlogP. The fragment Nnot
%A%A is a specific case of the A$A!A$A fragment. Two fragment patterns
(pattern1 and pattern2) (Fig.
2
), common to many potent blockers, were discovered
through the mapping of the descriptors selected with the threshold at 1
m
M. The
fragments of pattern1 are related to the ACH
2
AACH
2
A and ACH
2
AAACH
2
A
fragments, while the fragments of pattern2 are characterized by a nitrogen atom
bound to an aromatic ring.
A series of 246 descriptors and the na¨ve Bayes classification technique were
used by Sun et al. [
69
] A training set of 1,979 compounds from Roche and generic
molecular descriptors and fingerprint-based descriptors were used to generate a
classification model. The model achieved an ROC accuracy of 0.87. The model,
tested with an external dataset, predicted correctly 58 out of 66 molecules. The
fingerprint-based na¨ve Bayes model was built using FCFP_6, a 2D-descriptor
where each heavy atom of the molecule is described by a string of extended
connectivity values, together with physicochemical descriptors such as AlogP,
molecular weight, number of hydrogen bond donors and acceptors, and number
of rotatable bonds. The model achieved an ROC accuracy of 0.93, indicating that
the classification accuracy of the fingerprint-based model is higher than the one of
the atom-typing model. The predictive accuracy of both models is similar, as shown
by the predictions of the 66 compounds of the test set. Analysis of the most
important atom-types indicates that some particular fragments might play an
important role for hERG inhibition. The presence of acidic groups abolishes
hERG blocking, while basic groups such as piperidines and piperazines are impor-
tant for hERG blockage. They also observed that compounds, which branch imme-
diately after an aromatic moiety have the tendency to be hERG blockers.
SVMs combined with the pharmacophore-based GRIND descriptors were used
by Li et al. [
41
] to design a classification model. To generate the GRIND
descriptors, 495 compounds were docked into a homology model of the hERG
channel in the open state. For every molecule the best scoring pose was selected
to calculate the pharmacophoric GRIND descriptors, which were combined with
the SVM to generate classification models using cutoff values of 1
m
m
M, 5
m
M,
10
M. Four probes were selected to calculate the
pharmacophore-based GRIND descriptors: DRY (representing the hydrophobic
interactions), O sp
2
carbonyl oxygen (representing H-bond acceptor), NH neutral
m
M, 20
m
M, 30
m
M, and 40
m