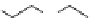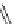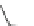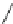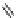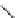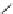Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
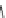
Ralfinamide (Fig.
4
): while the ability of ralfinamide as analgesic is still under
investigation, the result obtained in animal models for neuropathic pain is encour-
aging [
141
].
Lidocaine (Fig.
4
): lidocaine is a local anesthetic of wide use and its intravenous
injection has proven to be effective in reducing neuropathic pain [
142
] and diabetic
pain [
143
]. It was also demonstrated that subcutaneous injection of this drug
reduces cancer-related neuropathic pain in patients, who are insensitive to opioid
treatment [
144
]. It is also important to highlight phenomenon that occurs in patients
treated systemically with lidocaine. After brief exposures to the drug, patients
report days or even weeks of pain relief. This observation is supported by data
from animal models [
133
,
134
].
Oxacarbazepine (Fig.
4
): oxacarbazepine is a derivative of carbamazepine useful
in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia and diabetic neuropathies [
145
,
146
].
Nevertheless, it seems to lack the severe side effects typically induced by carba-
mazepine; in fact, oxacarbazepine was developed to avoid hepatic enzyme induc-
tion while retaining anticonvulsant activity of carbamazepine [
146
,
147
].
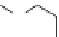
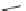
Amitriptyline and tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) (Fig.
4
): amitriptyline is a
TCA recently used for neuropathic pain by virtue of its capability to block sodium
channels [
148
]. It was demonstrated the drug capacity to relief patients from
diabetic neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia [
135
,
149
,
150
]. Moreover, a large
number of TCAs are commonly used in the treatment of neuropathic pain and other
chronic pain states [
135
,
151
]. They bind, similar to LAs, to the inactivated state of
VGSCs, although experimental evidences demonstrated that there are differences
between the two classes of drugs to relieve pain [
148
].
Lacosamide (Fig.
3
): lacosamide is a new anticonvulsant, which is thought to
bind to a novel site of action that enhances slow inactivation. Lacosamide displays
enhanced channel inhibition, and it has provided promising results in the treatment
of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy [
106
].
O
C
H
3
H
N
H
2
N
H
F
N
O
O
N
O
NH
2
O
ralfinamide
lidocaine
oxcarbazepine
CH
3
CH
3
OCHe
N
O
O
Cl
N
H
OCH
3
amitriptyline
A-803467
Fig. 4 Sodium channel blockers