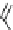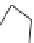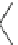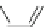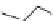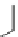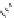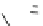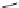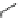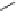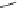Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
[
95
]. Phenytoin is a weak blocker of VGSCs at hyperpolarized membrane potentials
and low rates of channel activation, but its inhibitory action is greatly enhanced by
sustained membrane depolarization and during high frequency channel activity
[
96
]. As experimentally demonstrated, closed VGSCs, which are predominant at
hyperpolarized membrane potentials, have a low affinity for phenytoin, whereas
inactivated channel states, which are prevalent at depolarized holding potentials
and during high frequency channel activation, bind phenytoin in low micromolar
range [
95
,
96
]. Voltage-dependent and frequency-dependent inhibition suggests a
basis for the ability of phenytoin to suppress seizures while having minimum effects
on cognition. According to this hypothesis, phenytoin only weakly suppresses Na
+
currents during the intervals between seizures, in which neurons depolarize tran-
siently and fire single or short bursts of action potentials. Otherwise, during
seizures, neurons have prolonged discharges of action potentials riding on sustained
depolarizing episodes, which is the optimum condition for phenytoin inhibition of
VGSC activity.
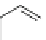
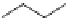
Carbamazepine (Fig.
3
): carbamazepine, similar to phenytoin, inhibits VGSCs in
a voltage-dependent and frequency-dependent manner at clinically relevant
concentrations and it is one of the major AED for partial seizures and generalized
tonic-clonic seizures but it is not effective against absence seizures [
95
]. The main
mode of action of carbamazepine is to block sodium channels during rapid, repeti-
tive, sustained neuronal firing. Hence, this drug might be more effective than
phenytoin at inhibiting seizures characterized by relatively brief depolarizing shifts;
this could explain the better responses of certain patients to phenytoin while others
are more effectively treated with carbamazepine.
O
O
HN
N
NH
O
N
O
+
Na
-
O
O
S
O
H
2
N
O
2
phenytoin
carbamazepine
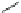
zonisamide
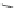
valproate
Cl
NH
2
OO
Cl
NH
2
O
O
O
F
3
CO
O
O
S
N
NN
N
NH
2
H
N
O
O
O
NH
2
O
lamotrigine
topiramate
riluzole
lacosamide
Fig. 3 Sodium channel blockers