Java Reference
In-Depth Information
reasonable number of retries. Similarly,
tryReleaseShared
increases the permit count,
potentially unblocking waiting threads, and retries until the update succeeds. The return value
of
tryReleaseShared
indicates whether other threads might have been unblocked by the
release.
CountDownLatch
uses AQS in a similar manner to
Semaphore
: the synchronization
state holds the current count. The
countDown
method calls
release
, which causes the
counter to be decremented and unblocks waiting threads if the counter has reached zero;
await
calls
acquire
, which returns immediately if the counter has reached zero and oth-
erwise blocks.
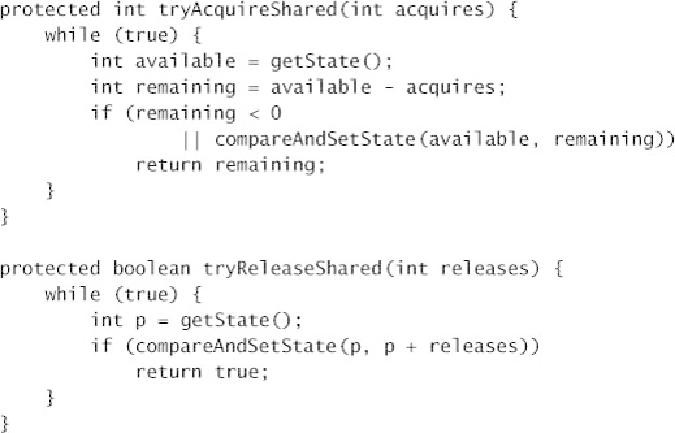
Listing 14.16.
Tryacquireshared
and
Tryreleaseshared
from
Semaphore
.
14.6.3. FutureTask
At first glance,
FutureTask
doesn't even look like a synchronizer. But
Future.get
has
semantics that are very similar to that of a latch—if some event (the completion or cancel-
lation of the task represented by the
FutureTask
) has occurred, then threads can proceed,
otherwise they are queued until that event occurs.