Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
B
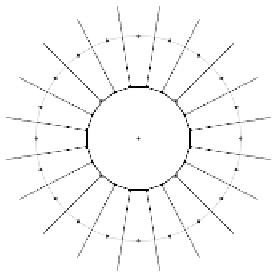
Fig. 13.12.
A Uniform Co-circular Barycentric Voronoi Diagram (UCBVD) for 20
co-circular sites. The barycentre is marked with a 'B'.
We identify the following UCBVD properties, where B denotes the
barycentre, BR is the barycentre region, C is the unit circle, and
d
is finite
except where noted:
Property 1: In the case of the circle being the unit circle then the
barycentre is the origin.
Property 2: The UCBVD barycentre region (BR) is a polygon with
d
edges.
Property 3: In a UCBVD, line segments drawn from the barycentre to
any Dimensional Anchor are perpendicular to the intervening
Voronoi edge of the BR.
Property 4: In a UCBVD, the BR is a regular polygon.
Property 5: A UCBVD has
d
+1 regions.
Property 6: As
d
ĺ the UCBVD BR tends towards a circle of radius
½ that of the enclosing circle C.
We establish these properties rigorously:
Proof of Property 1
: Construct vectors, based at the origin, and in the
direction of the DAs, of length 1/
d
. Pick any one of these vectors as a
starting point. Proceed counter-clockwise and add the next vector. This
gives us two edges of equal length, and the angle between them is 180 ޤ
(360/
d
) because we turn by 360/
d
as we traverse the edges. Continuing this
process yields
d
edges, all of equal length. The total of the internal angles is
equal to
d
(180 - (360/
d
)) = 180
d
- 360 = (
d
-2)180. Thus, traversing in this
manner produces a regular polygon that brings us back to the origin. Thus,
the sum of the vectors is the origin which is equivalent to the barycentre.


Search WWH ::

Custom Search