Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 6.20
Reconstructed surface profile of the connection rod. (
a
)SfPRDand(
b
) shape from
shading approach using stereo information, albedo estimated during the iteration process based on
all image pixels according to (
5.24
)
Fig. 6.21
Cross sections of the raw forged iron surface, compared to ground truth (RMSE in mm).
SfPRD and shape from shading approach using stereo information, albedo estimated during the
iteration process based on all image pixels according to (
5.24
)
data have shown that the standard deviation of the disparity amounts to 0
.
3pixel,
resulting in a standard deviation of 30
m of the resulting depth points. One of
the stereo cameras is equipped with a rotating linear polarisation filter and is used
to acquire the images required for SfPR according to Sect.
5.3.1
. Due to the highly
specular reflectance of the metallic surfaces, usually only a sparse set of depth points
can be reliably extracted using the blockmatching stereo algorithm.
For the raw forged iron surface of the connection rod, Fig.
6.16
a shows the inten-
sity and polarisation angle image and Fig.
6.16
b the triangulated stereo reconstruc-
tion result (d'Angelo and Wöhler,
2006
). The surface albedo was estimated based
on (
5.24
) during each step of the iteration process. We found that the RMSE between
the corresponding cross section extracted from our reconstructed three-dimensional
profile and the ground truth amounts to 45
μ
m (Figs.
6.20
a and
6.21
). If the shape
from shading approach is used such that polarisation information is not taken into
account, the RMSE is 163
μ
μ
m(cf.Fig.
6.20
b). The RMSE of the combined shape




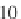































































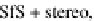


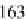































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search