Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 4.13
Image index vs. defocus measure
H
according to (
4.17
) for two different tracked image
features
1
3
with
ω
0
=
4
ω
max
, where
ω
max
is the maximum spatial frequency.
The amount of defocus increases with decreasing values of
H
. The defocus measure
H
is used to determine the index of the best focused ROI for each tracked feature in
the same manner as the grey value variance
χ
in Sect.
4.2.3.2
. Figure
4.13
shows the
behaviour of
H
for two different example features tracked across a sequence. The
value of
H
cannot be used for comparing the amount of defocus among different
feature points, since the maximum value of
H
depends on the image content. The
same is true for the grey value variance. Hence, both the integral
H
of the amplitude
spectrum as well as the grey value variance are merely used for determining the
index of the image in which a certain feature is best focused. Other defocus measures
may be used, as e.g. those regarded by Nayar (
1989
), but it depends on the individual
sequence as to which defocus measure is most useful to determine the sharpest ROI
of the sequence.
The PSF radius is then computed relative to the best focused ROI. The depth
z
is obtained by inverting the depth-defocus function
4
ω
max
and
ω
1
=
S
(z)
according to (
4.15
). The
encountered twofold ambiguity is resolved by using information about the direc-
tion of camera motion, which is obtained either based on a priori knowledge or by
performing a structure from motion analysis, e.g. according to Sect.
1.3
, yielding
information about the path of the camera. If the estimated value of
σ
is smaller than
the minimum of
(z)
obtains its minimum. For an example feature, the computed PSF radii and the in-
ferred depth values are shown in Fig.
4.14
, illustrating that the camera moves away
from the object at an approximately constant velocity.
An integration of the techniques of depth from defocus based on an image se-
quence acquired with a moving camera and structure from motion in order to ob-
tain an accurate and absolutely scaled three-dimensional scene reconstruction is de-
scribed in detail in Sect.
5.1
.
S
(z)
, the depth is set to the value of
z
at which the function
S









































































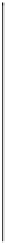















































Search WWH ::

Custom Search