Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
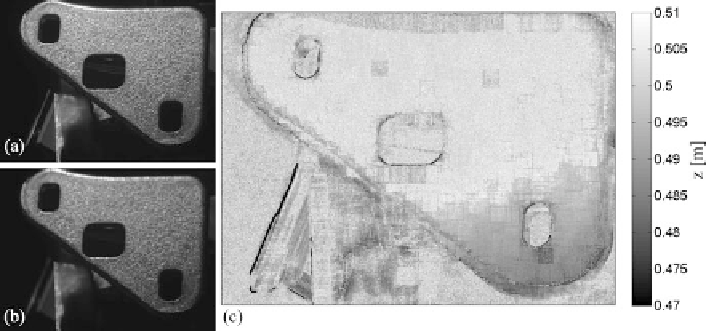
Fig. 4.12
Example of a depth map obtained with the depth from defocus approach based on two
images acquired with a stationary camera. (
a
) Sharp input image, acquired at
κ
=
8. (
b
) Unsharp
input image, acquired at
κ
=
2. (
c
) Resulting depth map. For the black pixels no depth value could
be computed. The
pixel grey
values are absolutely scaled in metres in the camera coordinate system
iris. The raw cast iron surface of this automotive part displays a sufficient amount
of texture to allow a reasonable estimation of the position-dependent PSF radius.
The depth from defocus method was calibrated according to the method illustrated
in Fig.
4.9
. The depth-defocus function shown in Fig.
4.10
was used to determine
the depth map in Fig.
4.12
c, clearly illustrating that the plane surface is tilted such
that its lower part is closer to the camera than its upper part.
Moving Camera
The description of the moving camera setting is adopted from
Kuhl et al. (
2006
), who extract salient features from the image sequence. These
features are tracked using the technique by Shi and Tomasi (
1994
) (“KLT tracker”,
cf. also Lucas and Kanade,
1981
), which is based on the Harris corner detector
(Harris and Stephens,
1988
). A ROI of constant size is extracted around each fea-
ture point at each time step. For each tracked feature, the best focused image has
to be identified in order to obtain the increase of defocus for the other images. It
is found that the grey value variance as a measure of defocus does not perform
well on features other than black-and-white corners. Instead, the amplitude spec-
trum
of the ROI extracted around the feature position is used by Kuhl
et al. (
2006
). High-frequency components of the amplitude spectrum denote sharp
details, whereas low-frequency components refer to large-scale features. Hence, the
integral over the high-frequency components can be used as a measure of the sharp-
ness of a certain tracked feature. However, since the highest frequency components
are considerably affected by pixel noise and defocus has no perceivable effect on
the low-frequency components, a frequency band between
ω
0
and
ω
1
is taken into
account according to
|
I
(ω
u
,ω
v
)
|
ω
1
I
(ω
u
,ω
v
)
dω
u
dω
v
H
=
(4.17)
ω
0
Search WWH ::

Custom Search