Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
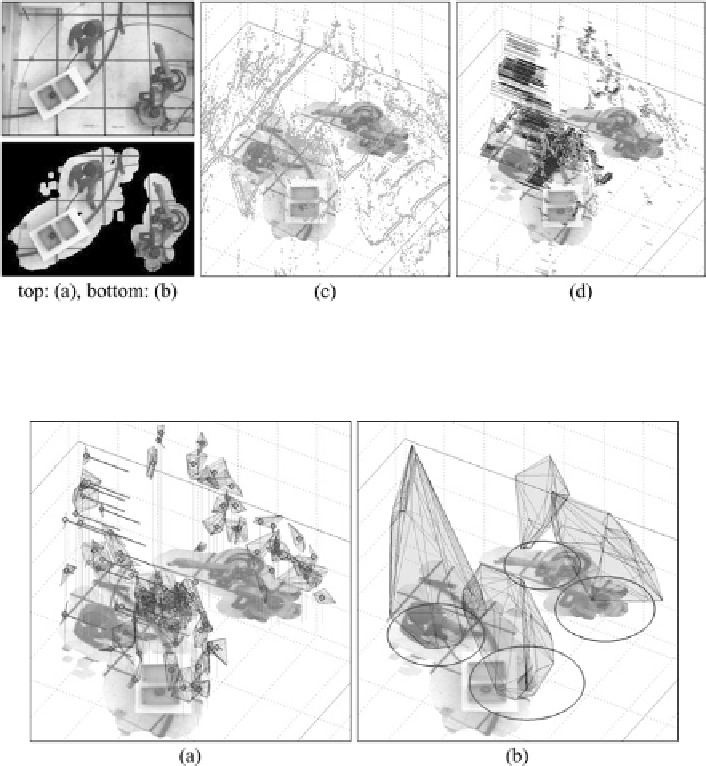
Fig. 2.20
(
a
) Original image (
left camera
). (
b
) Background subtracted image. (
c
) Full point cloud
obtained with the correlation-based stereo vision technique. (
d
) Reduced motion-attributed point
cloud
Fig. 2.21
(
a
) Over-segmentation and cluster velocities. (
b
) Objects with convex hull
2.3.4.2 Over-Segmentation for Motion-Attributed Clusters
To simplify the scene representation, we apply a hierarchical clustering algorithm,
recognising small contiguous regions in the cloud, based on features like spa-
tial proximity or homogeneity of the velocities. This procedure deliberately over-
segments the scene, generating motion-attributed clusters. By incorporating veloc-
ity information for clustering, we expect an improvement in segmentation at these
early stages of the algorithm, without the need for strong models to ensure separa-
tion of neighbouring objects. For clustering, we apply the complete linkage algo-
rithm to describe the distance between two clusters. The resulting hierarchical tree
is partitioned by selecting a clustering threshold and addressing each subtree as an
individual cluster (cf. Fig.
2.21
a). The criterion for selecting the threshold is the
Search WWH ::

Custom Search