Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
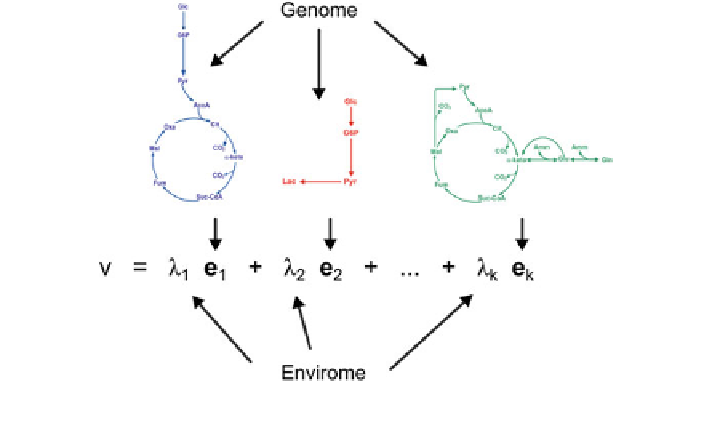
Fig. 4 Functional genomics versus functional enviromics. The genome sets the structure of
elementary modes. The activation of elementary modes is controlled by the environment
effective reduction of the initially very large number of elementary modes is
critical to decrease the complexity and to obtain a final parsimonious model.
In a set of recent studies [
11
,
13
] we investigated the systematic reconstruction
of metabolic processes based on regression analysis of elementary mode weighting
factors against measured environmental effectors. We have called this technique
''cell functional enviromics'' [
7
]. The principle is depicted in Fig.
4
. While the
genome sets the structure of elementary modes, the envirome sets the relative
contribution of each elementary mode to a given flux phenotype observation.
While functional genomics studies genome-wide cellular function reconstruction
through the collection and analysis of transcriptome or proteome data over time,
functional enviromics studies the reconstruction of cellular function through the
collection and analysis of dynamic envirome data. Functional enviromics applies
the following main steps:
(i)
Compute the elementary mode matrix, EM, from the microorganism meta-
bolic network.
(ii)
Acquire informative envirome data over time and organize it in the form of a
envirome data matrix X
¼
c
i
;
j
,aM
N matrix of M envirome factors, c
i,j
,
and respective measured flux data, R
¼
b
fg
,aM
q
0
matrix of measured
fluxes.
(iii) Apply systems-level analysis of dynamical envirome data X and R to find
relationships between environmental variables, c
i,j
, and elementary modes
weighting factors, k
i,j
.
In what follows, we describe a possible functional enviromics algorithm based
on the previous work by Ferreira et al. [
13
].
Search WWH ::

Custom Search