Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
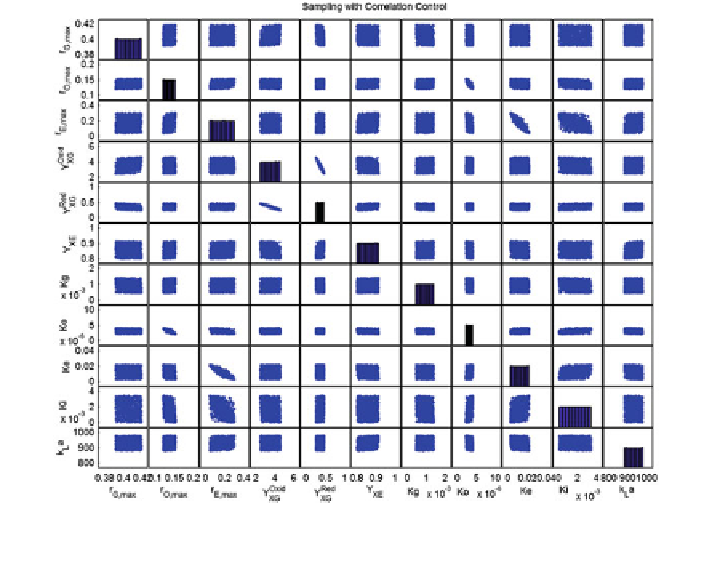
Fig. 5 Latin hypercube sampling for the model parameters, taking into account the correlation
between them
2.4 Uncertainty Analysis
Uncertainty analysis allows for understanding the variance of the model outputs as
a consequence of the variability in the input parameters. Such an analysis can be
performed using the Monte Carlo procedure, which consists of three steps:
(1) definition of the parameter space, (2) generation of samples of the parameter
space, i.e., combinations of parameters, and (3) simulation of the model using the
set of samples generated in the previous step. In this case study, a sample set of
1,000 combinations of parameter values was generated using the Latin hypercube
sampling procedure [
20
]. This sampling technique can be set up such that it takes
the correlations between parameters, i.e., information resulting from the parameter
estimation, into account (as explained by Sin et al. [
12
]). The correlation matrix for
all the parameters was estimated and is presented in Table
8
. For each parameter,
minimum and maximum values have to be defined: for the estimated parameters
the limits of the 95 % confidence intervals were used, while a variability of 30 %
around the default values was assumed for the remaining parameters.
The correlation between two parameters can take values between -1 and 1.
A positive correlation indicates that an increase in the parameter value will result
in an increase in the value of the other parameter as well. On the contrary, a
negative value indicates an inverse proportionality. In Fig.
5
, the sampling space is
illustrated by scatter plots of combinations of two parameters. A high correlation
Search WWH ::

Custom Search