Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 1.1 Size range of
nanomaterials in the food
sector
Structures
Diameter or length (nm)
DNA
12
Glucose
21-75
Liposome
30-10,000
LDH
40-300
Amylopectin
44-200
Casein micelle
60-100
PLA nanosphere
100-300
Zein
200
Cubosome
500
Nanosensors
1,000
<
Source
: Momin et al. (
2013
)
Fine emulsion droplets, nanoparticles
(inorganic) Solid-lipid nanoparticles
Self-assembly of molecules; liposomes,
surfactant micelles
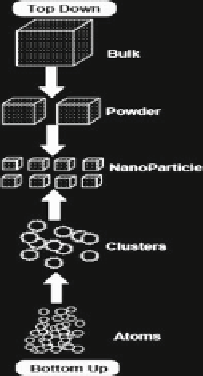
Fig. 1.1 Top-down and bottom-up approaches for nanomaterials manufacturing
Owing to the greater surface area of nanoparticles per mass unit, they are
expected to be more biologically active than larger-sized particles of the same
chemical composition. This offers several perspectives for functional food appli-
cations (Sozer and Kokini
2009
).
1.5 Natural Self-Assembled Nanostructures in Foods
A key area of application of nanotechnology in food processing involves the
development of nanostructures (also termed as nanotextures) in foodstuffs. Many
natural foods have nanoscale components. Their properties are determined by their
structure. These have been eaten safely for generations. In normal food processing,