Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
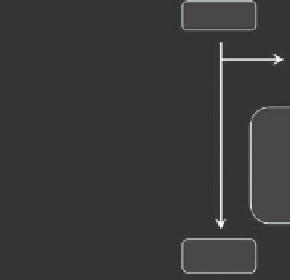
(a)
M(OR)
n
+ M'(OR)
n
or M(OR)
n
+ M'(O
2
CR)
n
+ ....
Solvent
(alcohols)
Additives-prevent precipitation
(acetylacetone, glycols, amines)
Imprortant factors-
solution viscosity,
rate of dipping, etc.
Dip-coating of substrate
Linkage of metal centers via
hydroxide (M-OH-M), oxide
(M-O-M) or alkoxide bridges
Hydrolysis,
polymerization
Sol forms on substrate
Dispersion of discrete colloidal
particles (10-1000 Å)
Destabilization of sol
Gel
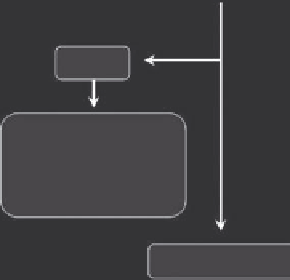
(b)
Gel
Drying
Monoliths
-minimize
stress caused by
volume change
Films
-faster drying
rates possible
Dry gel
Firing
Many processes-
combustion of organics,
dehydration
(polymerization), etc.
Oxide film (<1 µm)
FIGURE 2.6
(a) Chemistry of sol-gel process based on alkoxide route, (b) process covering the process from gel formation to
the final oxide nanocoating.

Search WWH ::

Custom Search