Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
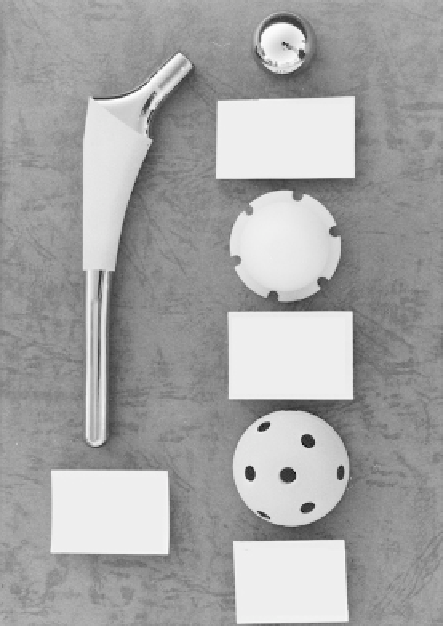
Head
CoNiCrMo alloy
(ASTM F562)
HAC
Insert
UHMW PE
(ASTMD 4020)
HAC
Stem
Ti6Al4V ELI
(ASTMF 136)
Acetabular cup
Ti6Al4V ELI
(ASTM F136)
FIGURE 6.1
Artificial total hip prosthesis includes stem, head insert, and acetabular cup.
alloys because of the compatibility between elastic moduli of bone and that of the Ti
alloy is important in order to avoid a difference in deformation between bone and the
implant when stress is applied. Therefore, clinical application of plasma-sprayed HACs on
Ti-6Al-4V alloy has the potential as an implant material not only because HA can bond
physicochemically with surrounding bone [4,17,38] and promote bone growth onto its sur-
] and promote bone growth onto its sur-
face [39-41], but also due to the excellent corrosion resistance and lower elastic modulus of
Ti alloy compared to 316L stainless steel and cobalt chromium alloys [42-44].
However, the high temperature and enthalpy employed during the plasma-spraying
process will result in large-scale dehydroxylation and decomposition effects of crystal-
4,17,38] and promote bone growth onto its sur-
,17,38] and promote bone growth onto its sur-
17,38] and promote bone growth onto its sur-
,38] and promote bone growth onto its sur-
38] and promote bone growth onto its sur-
of crystal-
line HA phase within the sprayed coatings [45,46]. Plasma-sprayed HACs with a higher
content of impurity phases and amorphous calcium phosphate will increase higher dis-
solution rate than crystalline HA in aqueous solutions and body fluids. It results in some
problems with decreasing the structural homogeneity and the degradation of mechanical
properties in the firm fixation between the implant and surrounding bone tissue [47,48].
Furthermore, clinical studies have indicated that the release of particles and subsequent
inclusion will result in fretting and abrasive wear behaviors between the implants and the
surrounding bone [21,49-51]. Therefore, decreasing the content of impurity phases and
amorphous calcium phosphate are rather important for the long-term biological stability
of plasma-sprayed HACs.
large-scale dehydroxylation and decomposition effects of crystal-
-scale dehydroxylation and decomposition effects of crystal-
scale dehydroxylation and decomposition effects of crystal-
dehydroxylation and decomposition effects of crystal-
effects of crystal-

Search WWH ::

Custom Search