Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
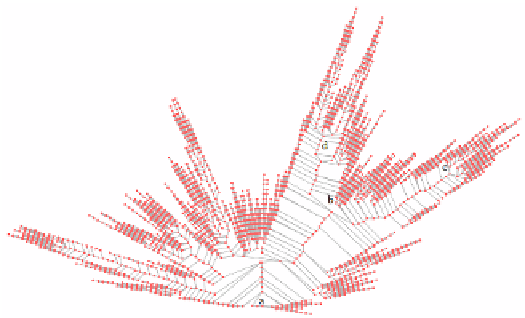
with 7472 nodes and 7471 edges of the t10n8 dataset
Fig. 3.
Poly-tree w
5
Conclusions
In this paper we presented
to identify branches in poly
of the problem into a netwo
The poly-tree model u
algorithm shrinks the data
heuristics were presented to
Back-and-Forward Heuristi
the visualization is obtained
also all of the most importa
We believe Ramex is v
provides a holistic view of
visualization benefits for t
results and avoids the
con
Secondly, the algorithm
environments, with high ve
implementation of Ramex
the storage of the large even
an instance of the network,
a new Sequence Mining algorithm called Ramex in or
y-trees. The algorithm has two phases: the transformat
ork, followed by the search of sequences.
uses condensed data structures. The first phase of
a without losing information. In the second phase, t
o find trees and poly-trees, the Forward Heuristic and
ic both inspired in the Prim algorithm. The simplicity
d using the poly-tree structure that shows all the events
ant event paths, without overlays, by-passes or cycles.
very useful in Pervasive Information Systems. Firstly
the system, by retrieving the x-ray of the input data, w
the end-user. The accumulation of data produces sta
ncept drift
as is common in micro-patterns approach
performance enables its implementation in Big D
elocity in the updates. To deal with data stream the onl
allows the accumulation of data in the network, avoid
nt logs. In the meantime, the tree generation could run o
according to the specifications of the user.
rder
tion
the
two
the
y in
and
y, it
with
able
hes.
Data
line
ding
over
References
1.
van der Aalst, W.: Proc
Business Processes. Sprin
2.
van der Aalst, W.: Mine Y
Real Value. In: Keynot
Utrecht, The Netherlands
cess Mining - Discovery, Conformance and Enhancement
nger (2011) ISBN 978-3-642-19344-6
Your Own Business: Using Process Mining to Turn Big Data
e 21st European Conference on Information Systems, EC
(2013)
t of
into
CIS,
Search WWH ::

Custom Search