Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
root hairs (Wissuwa et al. unpublished). Like-
wise, a gene-expression analysis of roots using
Agilent arrays did not reveal differential expres-
sion of P-starvation genes in the Nipponbare-
Pup1
NILs (Pariasca-Tanaka et al. 2009).
Since the function of
Pup1
could not be
deciphered, the genomic region was sequenced
using Kasalath BAC clones to identify the major
determinant of tolerance and gain insight into
the tolerance mechanisms. The sequence of the
Kasalath
Pup1
and flanking regions is available
under gene bank accession number AB458444.
Comparative sequence analyses between the
Kasalath
Pup1
locus (Kas-Pup1) and the syn-
tenic region in the Nipponbare (Nip-Pup1) ref-
erence genome revealed major differences in
size and gene content (Heuer et al. 2009). The
main structural difference between the two
Pup1
genomic regions is a large (
(Figure 5.3a). Based on an in silico analysis,
sixty-eight gene models were predicted, includ-
ing more than 54% transposable elements (TEs;
Heuer et al. 2009). Because many predicted
genes showed partial sequence similarity to TEs
and functional genes, extensive sequence analy-
ses were required to validate the gene models
and to short-list a set of candidate genes. To
determine whether the short-listed genes were
expressed, gene expression analyses were con-
ducted using Nipponbare NILs with and with-
out the
Pup1
locus grown under P-fertilized
(
P) and P-deficient (-P) conditions. Based on
this comprehensive gene assessment, five genes
were eventually short-listed, including a fatty
acid alpha dioxygenase (
OsPupK04-1
), a hypo-
thetical protein located in reverse orientation
within an intron of this gene (
OsPupK05-1
), a
dirigent gene (
OsPupK20-2
), and a hypotheti-
cal protein (
OsPupK29-1
), as well as a protein
+
∼
90 kb) insertion-
deletion (INDEL) that is absent in Nipponbare
Nipponbare (~150 kb)
(a)
INDEL
Kasalath (~270 kb)
Kasalath gene
models (# 68)
(b)
K01 K04/5 K20 K29
co-dominant
K41-43 K46,48 K52 K59
dominant
(c)
K46-1
K20-2
Bsp
K29-1
N N
Kas
N N
Kas
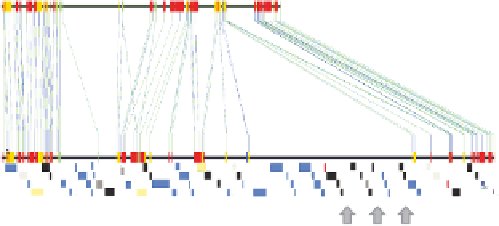
Fig. 5.3.
Genomic sequence of the
Pup1
region and gene-specific markers.
The
Pup1
genomic
region derived from sequencing of Kasalath BAC clones was aligned with the corresponding region
in the Nipponbare reference genome (
a
). Some regions show partial sequence similarity (indicated by
vertical lines). A large insertion/deletion (INDEL) specific to Kasalath
Pup1
is indicated. Sixty-eight
Kasalath gene models (indicated by different-size blocks) were predicted in silico and validated gene
models were targeted for the design of allele-specific codominant and dominant markers (
b
). Three
ideal
Pup1
markers were identified and are recommended for breeding applications (
c
). Details and
references are given in the text. For a color version of this figure, please refer to the color plate.






Search WWH ::

Custom Search