Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
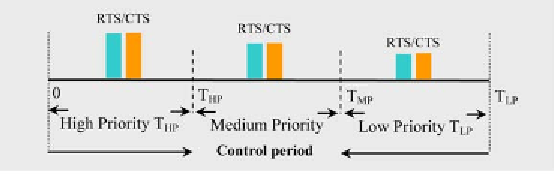
Figure 4. The structure of the control period
c. The Priority Queues
and QoS Support
•
Low priority T
LP
: it is reserved to two-hop
neighbors or to low priority packets (best-
effort, background).
H-MAC protocol uses the priority queue concept
inspired from the IEEE 802.11e protocol to sup-
port the QoS requirements. Each node maintains
3 priority queues:
The transmission rule:
according to Figure
4, as a node
i
acquires data to transmit, it checks
whether:
• It is the owner of the current slot on its
destination's channel or it has a high prior-
ity packet.
• It is the one-hop neighbor of the owner of
the slot on its destination's channel or it has
a medium priority packet.
• It is the two-hop neighbor of the owner of
the slot on its destination's channel or it has
a low priority packet.
•
High priority queue
: contains real time pack-
ets (we can also integrate transient traffic i.e.
not originated form the current node).
•
Medium priority queue
: contains audio and
video packets.
•
Low priority queue
: contains best-effort and
background packets.
d. Explicit Contention
Notification (ECN)
b. The HCL Mode
ECN messages notify two-hop neighbors not to
act as hidden terminals to the owner of each slot
when contention is high. Each node makes a lo-
cal decision to send an ECN message based on
its local estimate of the contention level (Figure
5). The estimation is obtained by the noise level
of the channel. ECN is similar to RTS/CTS in
CSMA/CA. But the difference is that HCL uses
topology information (i.e., slot information) to
avoid two hop collision. The cost of ECN is also
far less than RTS/CTS since it is triggered only
when contention is high.
In HCL, we have only the first and the second
period. Consequently, a node can compete in the
current slot if and only if:
• It is the owner of the slot on its destination's
channel or it has a high priority packet.
• It is the one-hop neighbor of the owner of
the slot on its destination's channel or it has
a medium priority packet.
After the control phase, all nodes that have
already succeed their negotiation switch to the
channel of their destination nodes and start the
data packet transmission for the rest of the slot.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search