Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
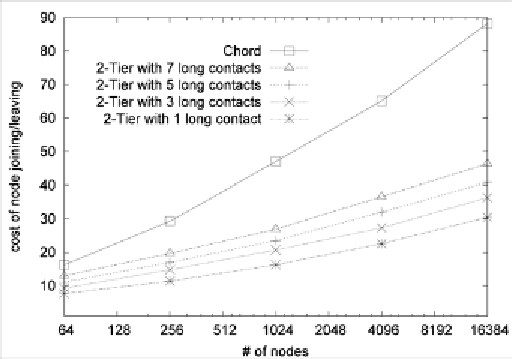
Figure 7. Cost of node joining/leaving
to the number of nodes in each semantic cluster.
Figure 7 plots the average number of messages
incurred when a node joins or leaves the network.
The results show that our system reduces the cost
of node joining/leaving significantly as compared
to Chord whose update cost of node joining/leav-
ing is
O(log
2
N)
, where
N
is the total number of
nodes in the network. This is also the effect of
clustering, i.e., the number of nodes in a semantic
cluster is much smaller than the number of nodes
in the whole network. Hence, each node needs
maintain a smaller size of finger table in our
system as compared to Chord.
differ from one to another. When a peer starts, it
first goes through the semantic clustering mapping
process to identify which semantic cluster to join.
The mapping process is done by iterating each of
the RDF data triples and identifying its correspond-
ing semantic cluster. Then the peer chooses the
major semantic cluster to join. On average, the
program initialization process takes about 4.26
seconds, and the mapping process for each RDF
data triple takes about 0.251 ms. The initialization
process involves reading and merging the ontol-
ogy files stored locally and generating internal
data structures for mapping. It is done only once
when a peer starts and is only repeated if there
is a change in these ontologies. Upon joining the
network, each node creates and maintains a set
of peers in its routing table. The joining process
involves initiating the Join message, connecting
to those nodes in the JoinReply message received
and registering its reference if needed. The results
for different steps in the bootstrap process are
summarized in Table 1.
We evaluate the dynamic characteristic of the
network in our prototype by forcing peers to join
and leave different semantic clusters randomly.
Cluster splitting/merging may occur when the
cluster size is greater/lower than the default size.
PROTOTYPE MEASUREMENT
Aim to explore practical issues in our proposed
system, we develop a prototype system. We are
interested in finding the bootstrapping behavior
and dynamic characteristic of the network.
In the prototype, peers run on Pentium 800MHz
desktop PCs with 256MB memory. The network is
constructed when peers randomly join the network.
We test the bootstrap process by connecting all the
peers to the network in different joining sequences;
hence, the structure of the network obtained may
Search WWH ::

Custom Search