Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
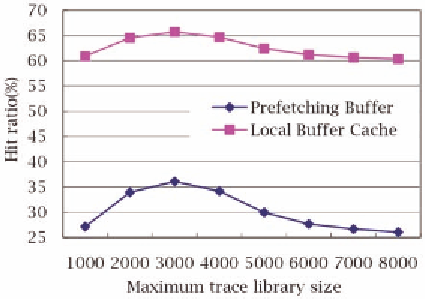
Figure 7. Hit ratio with different maximum trace
library size
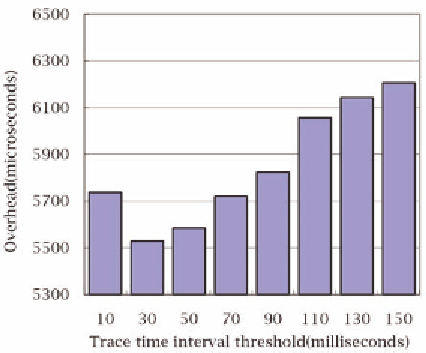
Figure 8. Reading overhead with different trace
time interval threshold
or networked file systems (Chang,
et al.
, 1999;
Dahlin,
et al.
, 1994; Jiang,
et al.
, 2006; Sarkar,
et
al.
, 1996; Voelker,
et al.
, 1998), or remote RAM
disk respectively (Flouris,
et al.
, 1999). Unlike
network memory schemes, RAM Grid tries to
share the plentiful memory resources distributed
in a wide area network (Chu,
et al.
, 2006). It ag-
gregates resources in a large scale and avoids the
inadequate idle memory resources problem within
a single cluster, while it must also deal with the
dynamic and heterogeneous resources effectively
using a decentralized architecture.
The effect of prefetching mainly depends on
the prediction of the data access. For magnetic
disk I/O, the prediction is restricted in millisec-
ond level. It means that the prediction algorithm
should output a result in milliseconds; otherwise
the prefetching cannot speed up the I/O access.
Griffioen
et al
. build a directed probability graph
among the files (Griffioen,
et al.
, 1994), a directed
edge means that the files are opened very closely.
Using the probability graph, the system can predict
the next opened file with slight overhead, while
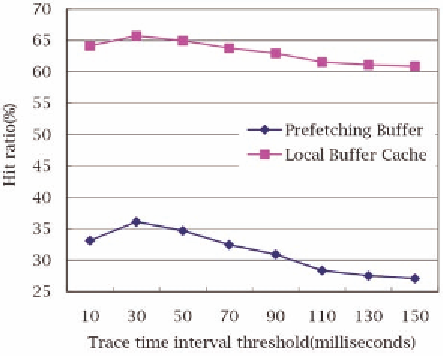
Figure 9. Hit ratio with different trace time interval threshold
Search WWH ::

Custom Search