Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
CONCLUSION
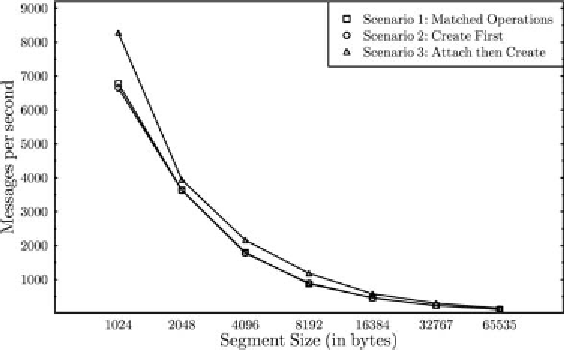
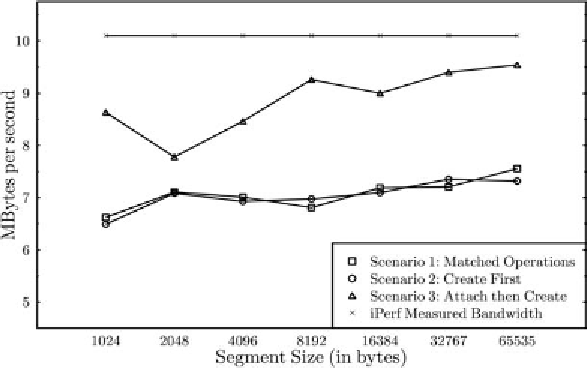
π-channel. This makes it possible for the writer
of that π-channel to transmit the channel segments
directly to the reader, showing a substantial im-
provement in the data transfer performance over
that of the first two scenarios. Furthermore, the
overlap of sends and receives results in better
utilisation of the available bandwidth.
We have presented π-Spaces/π-channels, a com-
munication mechanism for scientific workflows
on dynamic environments, where resources
may fail and network links may be disrupted.
The key feature of π-channels is persistence,
enabling communication despite process failures
or departures. This article presents its design and
implementation. In particular, we describe the
distributed algorithm showing how persistence
Figure 7. Measured message-send rates with a ping-pong benchmark
Figure 8. Measured bandwidth with a ping-pong π-Space/π-channels application. The horizontal bar
shows the measured bandwidth using iperf
2
Search WWH ::

Custom Search